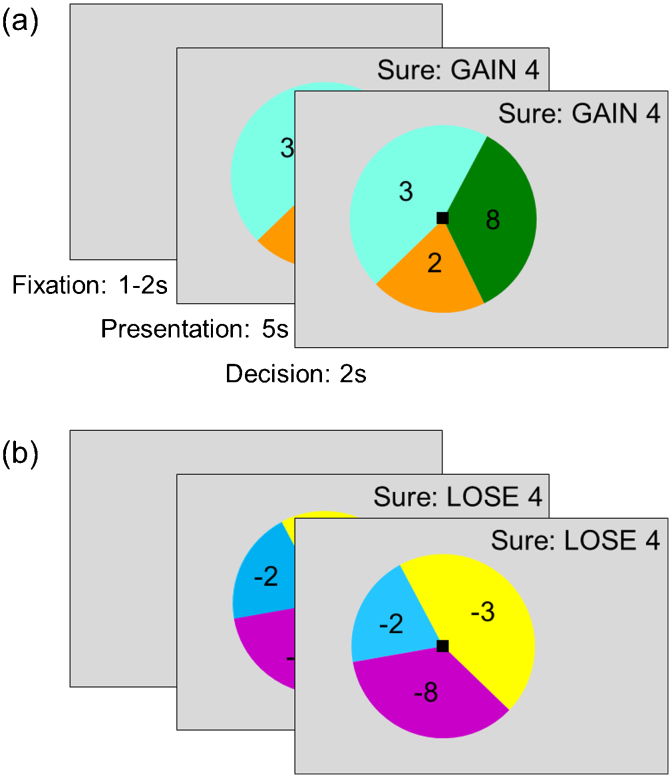
Fig. 1.
Experimental design. In each trial, participants were instructed to choose between a lottery and sure option. The lottery was represented by a pie chart with three segments corresponding to the three possible outcomes, with the size of each segment corresponding to the probability of that outcome occurring. The sure option was indicated on the upper right side of the screen. Half the trials involved winning points (“gain” trials) and half involved losing points (“loss” trials). (a) In each gain trial, participants chose either to accept a lottery (three varying possible outcomes, all ≥0) or reject it in favour of a sure gain of four points. (b) In each loss trial, participants chose either to accept a lottery (three varying possible outcomes, all ≤0) or reject it in favour of a sure loss of four points.