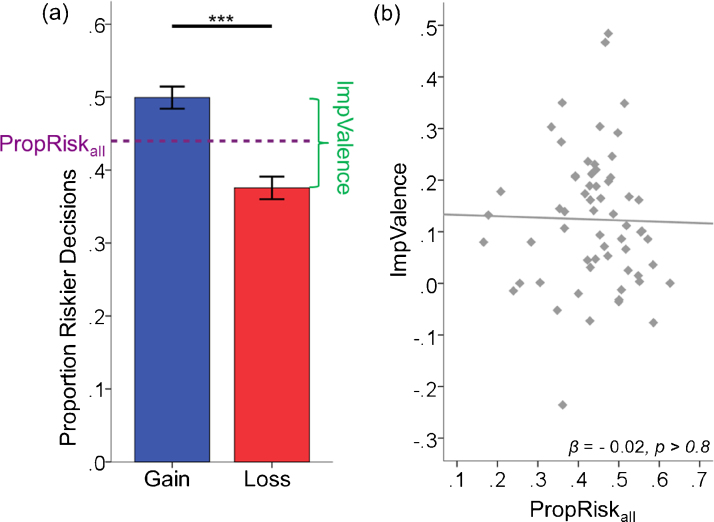
Fig. 2.
Risk and valence both influenced decisions, and individuals’ preferences for both were not associated (a) Individuals were significantly risk-averse overall (PropRiskall < 0.5) as opposed to risk-neutral. Valence (ImpValence = PropRiskgain − PropRiskloss) also significantly influenced decisions, with more gambling for gains than losses. (b) Individuals’ preferences related to risk (PropRiskall) and valence (ImpValence) were not associated. Error bars indicate standard error. ***p < 0.001.