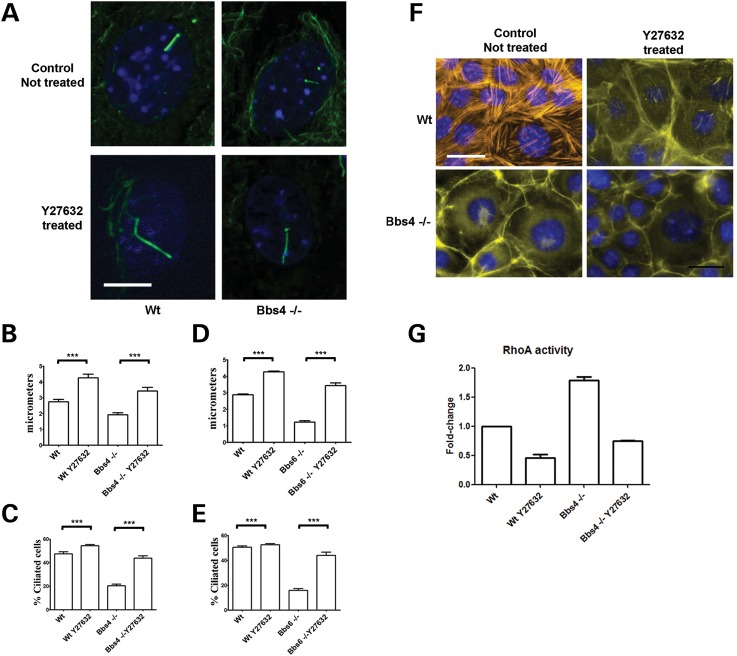
Figure 7.
Inhibition of the RhoA pathway with Y27632 rescues the actin cytoskeleton and cilia length in Bbs4 null cells. (A and B) Cilia of WT serum starved cells treated with Y27632 were longer (4.256 μm ± 0.2367) than untreated cells (2.746 μm ± 0.1527). Likewise in Y27632 treated Bbs4 null cells, cilia were almost twice as long as untreated cells (3.429 μm ± 0.2355 versus 1.923 μm ± 0.1321; P < 0.001). Scale bar 5 μm. (C) The number of ciliated Bbs4 null cells (43% ± 1.95) recovers to WT levels (54% ± 0.99) when treated with Y27632, P < 0.0001. (D) A similar result was obtained when Bbs6 null cells were treated with Y27632. WT-treated cilia were again longer (4.276 μm ± 0.04531 N = 29) than untreated cells (2.883 μm ± 0.04899 N = 32). Likewise in Y27632 treated Bbs6 null cells, cilia doubling the length compared with untreated cells (3.445 μm ± 0.1529 N = 31 versus 1.224 μm ± 0.08055 N = 24; P < 0.001). (E) The number of ciliated Bbs6 null cells (16% ± 1.38) recovers to WT levels (44% ± 0.99) when treated with Y27632, P < 0.0001. (F) There is a reduction in stress fibre aggregate formation in Bbs4 null cells following exposure to Y27632. Scale bar 30 μm. (G) RhoA activity of cells treated with 10 mm of Y27632 for 30 min. All data were normalized for WT RhoA activity. After the treatment, the levels of activated RhoA were reduced to a half in WT-treated cells (0.4614 ± 0.05629). We found the same reduction RhoA activity in Bbs4 null cells, from 1.788 ± 0.095 to 0.7475 ± 0.0053. ***P < 0.001.