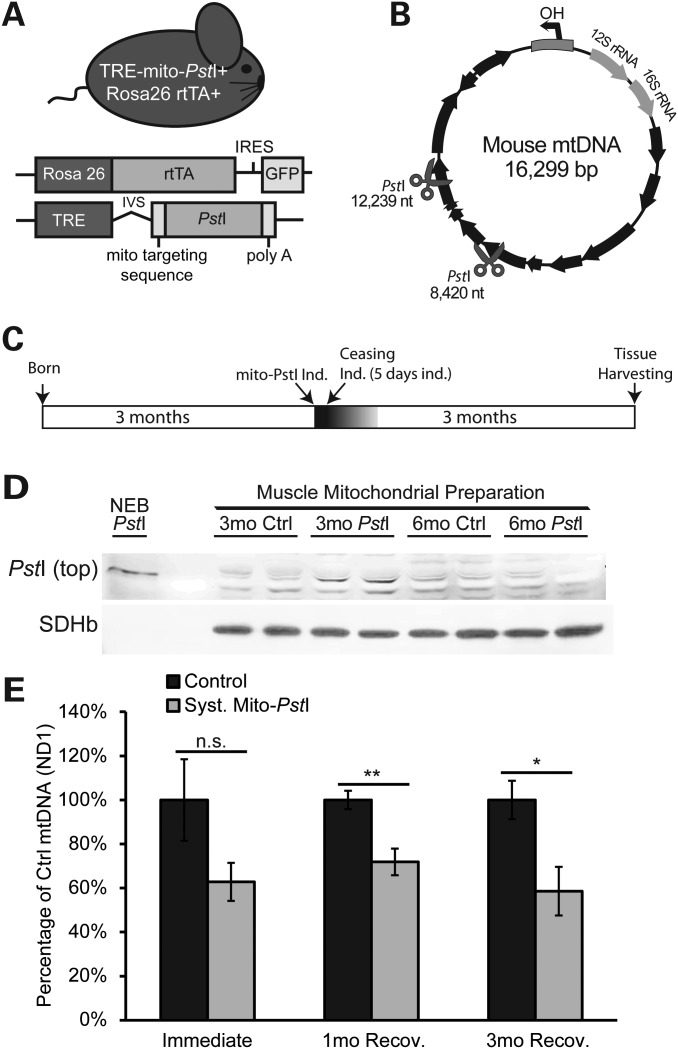
Figure 1.
Characterization of expression of mito-PstI in skeletal muscle of transgenic mice. (A) Schematic representation of the systemic mito-PstI mouse and the transgenic constructs. (B) MtDNA map showing the targeted sites of PstI (scissors). Black arrows denote protein-coding genes. (C) Schematic representation of mito-PstI induction and experimental paradigm: 5-day induction at 3 months of age, and up to 3 months follow-up after the induction. (D) Western blotting using an anti-PstI antibody to detect mito-PstI expression in mitochondrial extracts of gastrocnemius muscle from systemic mito-PstI mice after a 5-day induction at 3 months of age, and at 6 months of age. NEB (New England Biolabs) PstI restriction enzyme was used as a molecular weight control. Antibody against SDHβ was used as a loading control. (E) Real-time PCR quantification of mtDNA/nuclear DNA ratios of quadriceps from the systemic mito-PstI mice and age-matched controls after 5-day induction, 1 and 3 months recovery (n = 5 per group for ‘immediate’ and ‘3mo’ time points, and n = 4 per group for ‘1mo’ time point). An unpaired t-test was performed for each time point. Values are presented as mean ± SEM (*P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001).