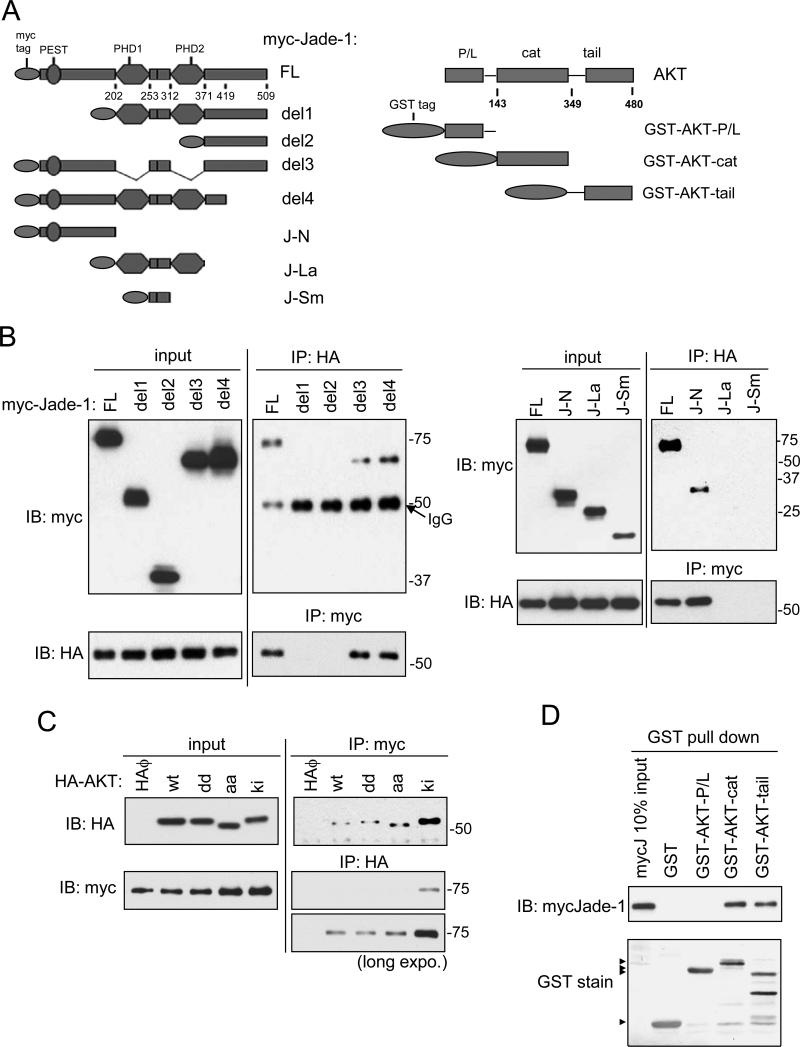
Figure 4.
The N-terminus of Jade-1 binds both the catalytic domain and the C-terminal regulatory region of AKT. A. Schematics of myc-tagged Jade-1 truncation constructs and GST-tagged AKT domain constructs. B. AKT binds the N terminus of Jade-1. HA-AKT was transiently cotransfected in HEK293T cells with myc-Jade-1 truncations (left panels: full length, del1, del2, del3, del4; and right panels: full length, J-N, J-La, J-Sm). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-myc antibody and then immunoblotted with anti-HA antibody, and vice versa. Whole cell lysates (10% of input) showed comparable expression of HA-AKT or myc-Jade-1 truncations across samples. C. Jade-1 shows increased binding to a kinase inactive AKT mutant. Myc-Jade-1 was transiently cotransfected with different forms of HA-AKT, wild type (wt); T308D/S473D (dd); T308A/S473A (aa); or K179M (ki). D. Jade-1 binds to the AKT kinase domain and the regulatory C terminus. Cell lysates with overexpressed myc-Jade-1 were incubated with bacterially expressed, purified GST fusion protein GST-AKT-P/L, GST-AKT-cat, GST-AKT-tail, or GST alone.