Fig. 1.
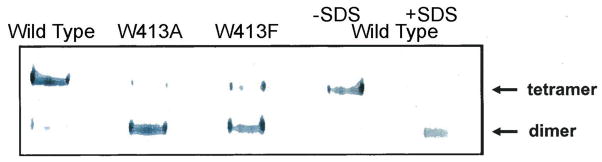
Native gel electrophoresis of wild-type and Trp413 mutant A2M. Samples were analyzed on a single native gel. The wild-type sample in the far right lane was made 2% in SDS to dissociate tetramers to disulfide-linked dimers.
The proteins were produced as follows: Chinese hamster ovary CHO-K1 cells were purchased from ATCC (catalog CCL-61, Manassas, Virginia, USA) and grown in DMEM (Gibco-BRL 10566-016, Life Technologies, Grand Island, New York, USA) containing 10% fetal calf serum. Cells were maintained in 5% CO2 and 5% oxygen. The human A2M gene sequence encoding wild type (WT), Trp413Ala, Trp413Phe was cloned into pcDNA 3.1 (+) (Invitrogen V790-20, Life Technologies, Grand Island, New York, USA). CHO-K1 cells were stably transfected with the expression vectors. The stably transfected cells were selected in DMEM with 10% FBS containing 3 mg/ml Geneticin (Invitrogen 10131-027). Selected cell lines were then grown in CHO serum-free culture medium (BioWhittaker 12-029Q, Walkersville, Maryland, USA) without Geneticin. After 73 h in culture, 30 ml of medium were collected and concentrated to 1.5 ml through a centrifugal filter YM10 (EMD Millipore, Billerica, Massachusetts, USA). The concentrated samples were subjected to native gel electrophoresis on a 6% Tris-glycine gel (EC6068, Invitrogen) run at 125 volts for 130 min at room temperature. Proteins were electroblotted to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (LC2002, Invitrogen), incubated with rabbit anti-human A2M as the primary antibody (DAKO A0033, DAKO, Carpinteria, California, USA) and an anti-rabbit IgG conjugated to alkaline phosphatase (475-1516, KPL, Gaithersburg, Maryland, USA) as the secondary antibody. A2M was visualized by incubation with nitro blue tetrazolium/5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate (50-81-08, KPL).
