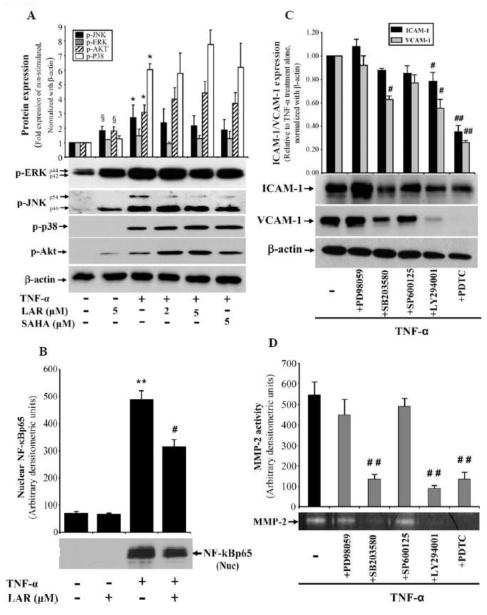
Fig. 5.
LAR coordinates with TNF-α to induce phosphorylation of AKT and MAPKs, but inhibits NF-κBp65 in RA synovial fibroblasts. (A) RA synovial fibroblasts (2 × 105/well) were pretreated with LAR (2-5 μM) or SAHA (5 μM) for 2 h, followed by stimulation with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 30 min in serum-free RPMI. Cells were lysed in extraction buffer containing protease inhibitors and utilized for the determination of p-ERK1/2, p-JNK, p-p38, and p-AKT in RA synovial fibroblasts using Western blotting. (B) Similarly treated RA synovial fibroblasts were utilized for preparation of nuclear fraction as described in Materials and Methods. Nuclear protein (15 μg) was used to analyze nuclear NF-κBp65. The intensity of the bands was quantified using Image-J software (NIH). (C&D) RA synovial fibroblasts were pretreated with the signaling inhibitors for ERK1/2 (PD98059, 10 μM), p38 (SB203580, 10 μM), JNK (SP600125, 10 μM), Akt (LY294001, 20 μM), or NF-κB (PDTC, 200 μM) for 2 h, followed by TNF-α stimulation for 24 h. Cells were lysed to study the expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1; conditioned media was collected to analyze MMP-2 activity using gelatin zymography. Values represent the mean ± SEM of 4-6 independent donors’ cells under similar conditions. §p<0.05 for NS vs LAR alone; *p<0.05 or **p<0.01 for NS vs TNF-α; ##p<0.01, TNF-α vs TNF-α plus inhibitor.