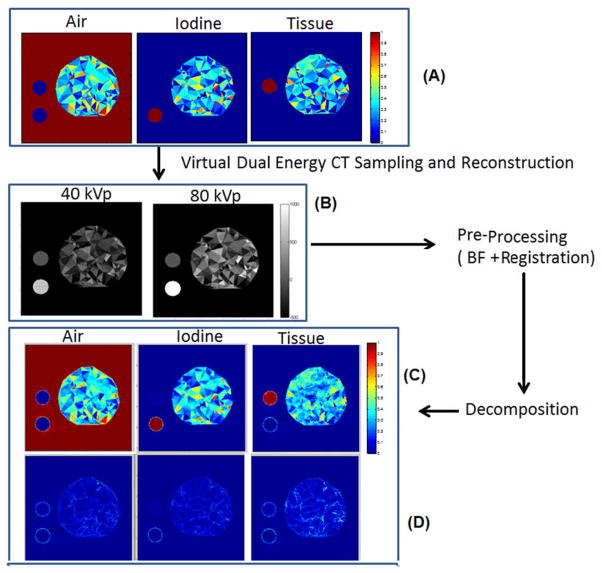
Fig. 2.
The simulation protocol and results. The phantom (A) made of random triangular structures with components of air, iodine and tissue was virtually irradiated to create noisy projections used to reconstruct CT images at 40 and 80 kVp (B). The CT images were preprocessed to lower their noise using bilateral filtering and registration. Next, the resulting images were decomposed to estimate the three material fractions (C). Each point on these graphs refers to one triangular structure in the phantom. The errors (i.e. A–C) of the method are shown by (D).