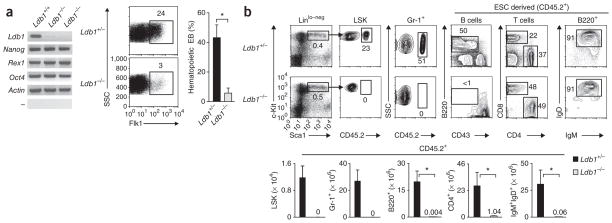
Figure 1.
Ldb1 is required for hematopoietic specification but is not essential for ESC maintenance. (a) RT-PCR analysis (left) of the expression of various genes (left margin) in Ldb1+/+ ESCs and Ldb1−/− ESCs (two independently generated clones); flow cytometry of cells in embryoid bodies at day 5 derived from Ldb1+/− or Ldb1−/− ESCs (middle); and frequency of Ldb1+/− or Ldb1−/− ESC-derived embryoid bodies (EB) at day 9 with hematopoietic satellite cells (right; identified by Giemsa staining of cytospin preparations). Numbers above outlined areas (middle) indicate percent Flk1+ cells. SSC, side scatter. *P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). Data represent one of two experiments (error bars, s.d.). (b) Frequency (above) and absolute number (below) of CD45.2+, LSK, granulocyte (Gr-1+) and B cells in the bone marrow and mature T cells in the lymph nodes and mature B cells (B220+) in the spleen of 8-week-old adult Ldb1+/− ESC and Ldb1−/− ESC chimeric mice. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas (above) indicate percent cells in gate; numbers above bars (below) indicate number of cells for bars not visible. Ig, immunoglobulin. *P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test). Data are representative of three experiments with six Ldb1+/− mice and three Ldb1−/− mice.