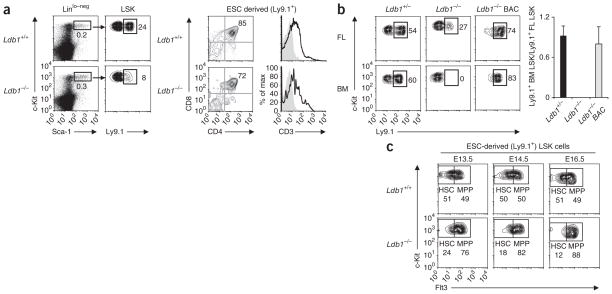
Figure 2.
Ldb1−/− hematopoietic progenitors are present in chimeric fetal livers but are unable to reconstitute hematopoiesis in irradiated recipients. (a) LSK cells in chimeric embryos at E13.5, generated by injection of Ldb1+/+ or Ldb1−/− ESCs into B6 (Ldb1+/+) blastocysts (left); ESC-derived (Ly9.1+) LSK cells were detected by staining for Ly9.1. Right, staining of gated Ly9.1+ (ESC-derived) thymocytes from chimeras at E18.5 with anti-CD4 plus anti-CD8 or anti-CD3. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas (left) and numbers in top right quadrants (right) indicate percent cells in gate. Data are representative of five experiments. (b) Flow cytometry of donor fetal liver (FL) cells at E15.5 and recipient bone marrow (BM) cells: Ldb1+/− or Ldb1−/− ESCs or Ldb1−/− ESCs reconstituted with a bacterial artificial chromosome containing Ldb1 (Ldb1−/− BAC) (Ly9.1+) were injected into Rag2−/− (Ly9.1−) blastocysts to generate chimeric embryos, followed by collection of fetal liver cells at E15.5 and injection into irradiated Rag2−/− (Ly9.1−) mice; 16 weeks later, bone marrow from recipient mice was analyzed for the presence of ESC-derived (Ly9.1+) LSK cells. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas (left) indicate percent Ly9.1+ LSK cells. Right, summary of data at left. Data are representative of four independent experiments (error bars, s.d.). (c) Flow cytometry of fetal liver cells from chimeric embryos at E13.5–E16.5, generated by injection of Ldb1+/+ or Ldb1−/− (Ly9.1+) ESCs into B6 (Ldb1+/+, Ly9.1−) blastocysts, assessing c-Kit versus Flt3 profiles on gated ESC-derived (Ly9.1+) LSK cells. Numbers adjacent to outlined areas indicate percent Flt3− LSK cells (HSC) or Flt3+ LSK cells (MPP). Data are representative of seven experiments with a total of two to three fetal livers per each time point.