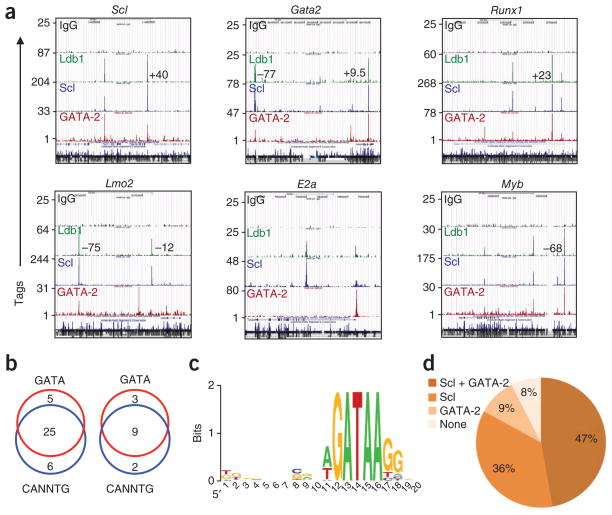
Figure 6.
Ldb1 complex–binding sites are present in a high percentage of genes critical for HSCs. (a) Selected genes involved in HSC maintenance with Ldb1 complex–binding sites in the promoter and/or gene body, as determined by ChIP-Seq analysis with control antibody to immunoglobulin G (IgG), anti-Ldb1, anti-Scl and anti-GATA-2. Numbers in plots indicate positions of binding sites at known distal regulatory elements. Sequence conservation track is shown at the bottom of each browser shot. Data are representative of two experiments. (b) Ldb1 complex–binding site fragments in the HSC-maintenance gene set (left) or in known regulatory elements near these genes (right) with conserved GATA motifs and/or E-box (CANNTG) motifs. Data are representative of two experiments. (c) Consensus sequence motif of sites containing a GATA-binding sequence in Ldb1 complex–binding sites at the promoter, gene body and/or known enhancers of HSC maintenance genes. Letter size indicates nucleotide frequency, scaled to the information content (measure of conservation) at each position; colors distinguish the nucleotides. Data are representative of two experiments. (d) Prevalence of Scl or GATA-2 binding at HSC gene sites identified by ChIP-Seq with anti-Ldb1. Data set includes the 53 DNA fragments in Supplementary Tables 1 and 3. Data are representative of two experiments.