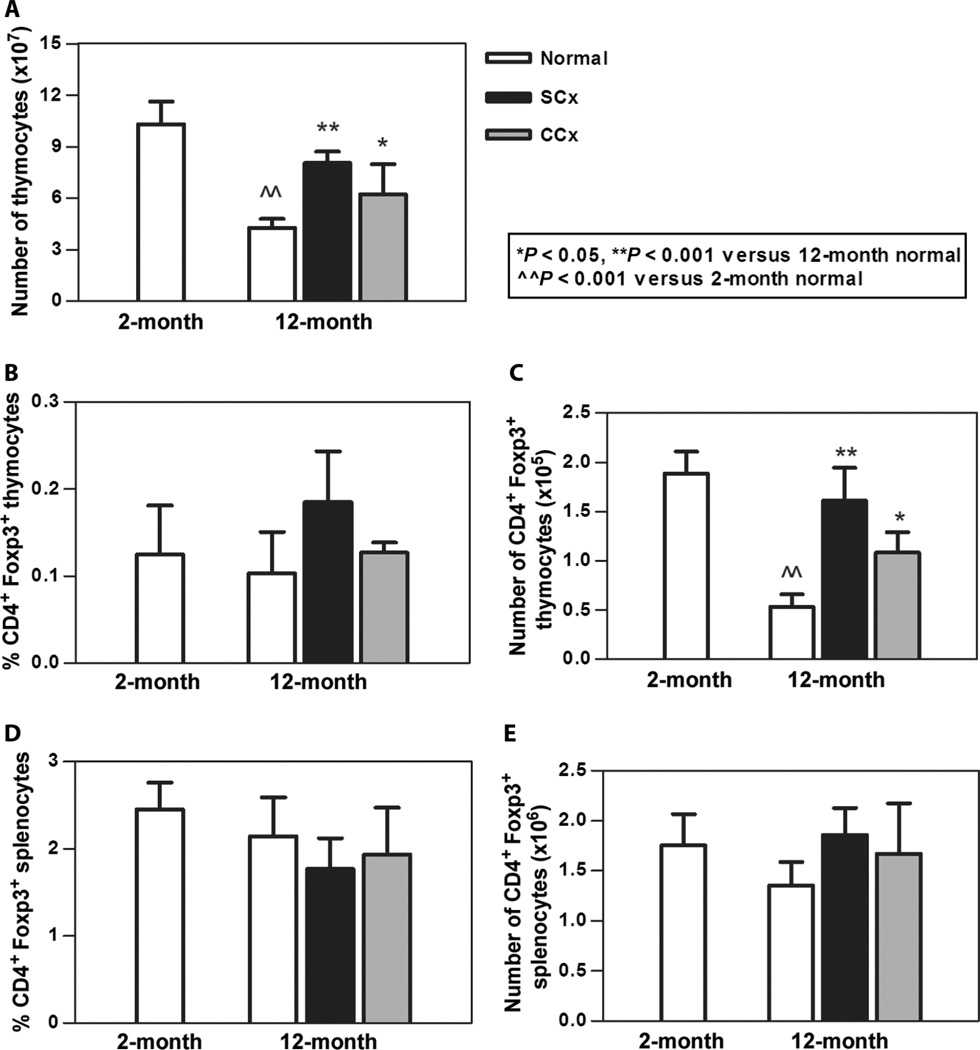
Fig. 5.
Chemical and surgical castration increased thymic cellularity and Treg numbers in aged mice. (A) Aged mice demonstrated an expected decrease in thymocyte number, whereas surgical and chemical castration resulted in an increased number of thymocytes. (B) Percentage of CD4+Foxp3+ thymocytes was not significantly increased. (C) Overall, there was an increase in the absolute number of Tregs. (D and E) Neither percentage (D) nor absolute number (E) of CD4+Foxp3+ splenocytes was increased. n = 3 to 5 animals per group for all groups.