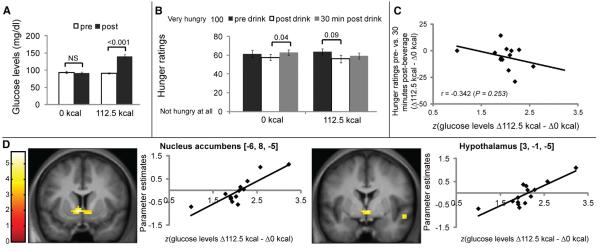
Figure 3.
Biological Utility Conditioning
(A) Subject-normalized plasma glucose levels increased significantly 30 min following ingestion of the 112.5 kcal, but not the 0 kcal, flavored beverage [two-way RM ANOVA, caloric load × time effect F(1,13) = 157.7; p < 0.001]. Post hoc paired two-sample t test, p < 0.001; NS, statistically nonsignificant; paired two-sample t test, p = 0.39. 112.5 kcal, 112.5 kcal beverage; 0 kcal, 0 kcal beverage.
(B) No overall decreases in hunger levels were observed after ingestion of the flavored beverages (two-way RM ANOVA, caloric load × time effect; p = 0.37); however, hunger levels increased significantly 30 min following ingestion of the 0 kcal, but not the 112.5 kcal, beverage (post hoc paired two-sample t test, p = 0.04).
(C) Consistently, changes in hunger levels were not correlated with changes in glucose levels. Data are shown as standardized (z score) changes in glucose. D112.5 kcal, changes in glucose levels (post- versus preconditioning session) for the 112.5 kcal beverage. Similar definition applies for Δ0 kcal.
(D) Coronal sections showing positive correlations between parameter estimates (PEs) associated with the statistical parametric map (SPM) contrast (112.5 kcal-paired [CS+] flavor minus 0 kcal-paired [CS−] flavor) and changes in plasma glucose levels (Δglucose, in mg/dl) following ingestion of the 112.5 versus the 0 kcal beverage during the conditioning sessions in the NAcc (MNI coordinates on the left are −6, 8, −5 [z = 3.9] and right = 9, 5, −8 [z = 3.5] [graph not shown for right NAcc]) and hypothalamus (MNI coordinates = 3, −1, −5; z = 3.7). Scatter plots displaying the relationship between changes in glucose levels versus PEs from these voxels are shown to the right of each coronal section. These peaks fall within a single cluster that was found to be significant at p < 0.05 FDR corrected at the cluster level across the whole brain (number of voxels in cluster k = 107). Color scale bars correspond to SPM t values. Changes in glucose are shown as standardized (z score). When liking was included as the first regressor and Δglucose as the second, minimal changes were observed in the results. In NAcc, the peak voxels were located at −3, 5, −5 (z = 3.81) and 9, 5, −5 (z = 3.35). In hypothalamus, the peak voxels were located at 3, −1, −5 (z = 3.7) and 3, −1, −5 (z = 3.9). As in the original analysis, these peaks fall within a single cluster that was found to be significant at p < 0.05 FDR corrected at the cluster level across the whole brain.
See also Table S1.