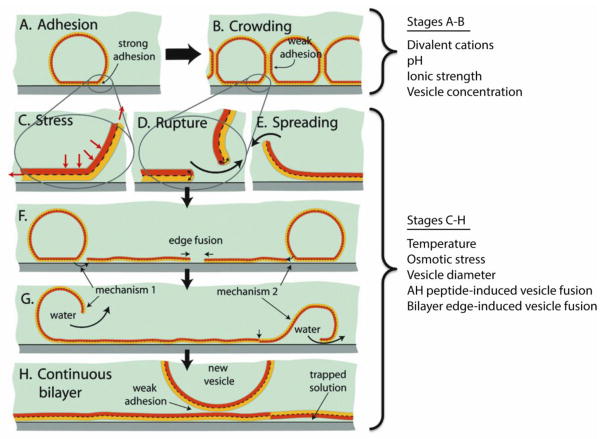
Figure 1.
Stages of SLB formation: (A) adhesion, (B) crowding, (C–E) rupture and spreading of bilayer patches that can expose either leaflet by mechanism 1 or 2, (F, G) coalescence of high energy edges and release of water/excess lipid, and (H) completed SLB. Additional vesicle adsorption to the SLB is typically weak and does not lead to their rupture or spreading. Experimental conditions and techniques that generally have the most pronounce effect on respective stages of SLB formation are listed to the right of the figure. Substrate type and chemical surface modifications are omitted from classification since these conditions generally affect the entire SLB formation process. Adapted with permission from reference [12*]. Copyright (2009) American Chemical Society.