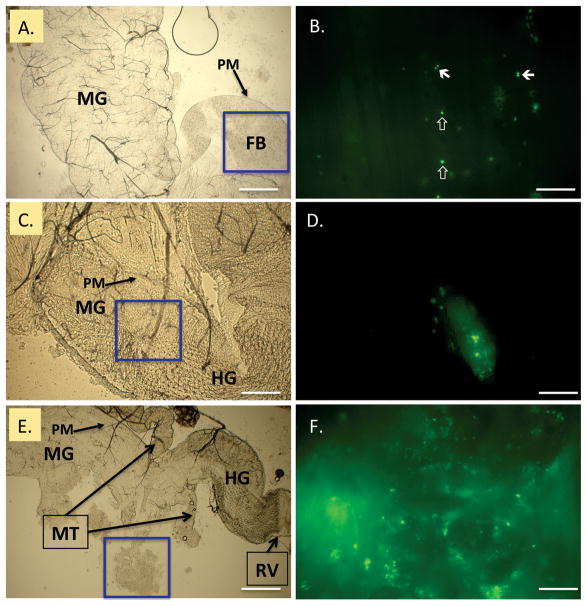
Fig. 1.
GFP-expressing Staphylococcus aureus in the house fly alimentary canal. Flies were fed 2.0 × 105 CFU, and bacteria were examined in dissected alimentary canals at 2, 4, and 6 h postingestion (PI). Epifluorescent microscopy (right, B, D, F) of blue boxed regions in bright field panels (left, A, C, E) revealed bacteria throughout the alimentary canal. Bacteria mainly appeared as single coccic and diplococcic forms as soon as 2 h (B., closed and open arrows, respectively), and were contained within food boluses (FB) in the peritrophic matrix (PM) of the midgut. Viable bacteria were visualized in the distal midgut (MG) and hindgut (HG) at 4 h PI. At 6 h PI, clumps of lysed and viable bacteria were released from the terminal open end of the PM, near the midgut/hindgut junction (E, boxed, freed during preparation and magnified for detail in F). MT = Malpighian tubules; RV = rectal valve. Scale bars: A, C, E, 200 μm; B, D, F, 20 μm. (Online figure in color.)