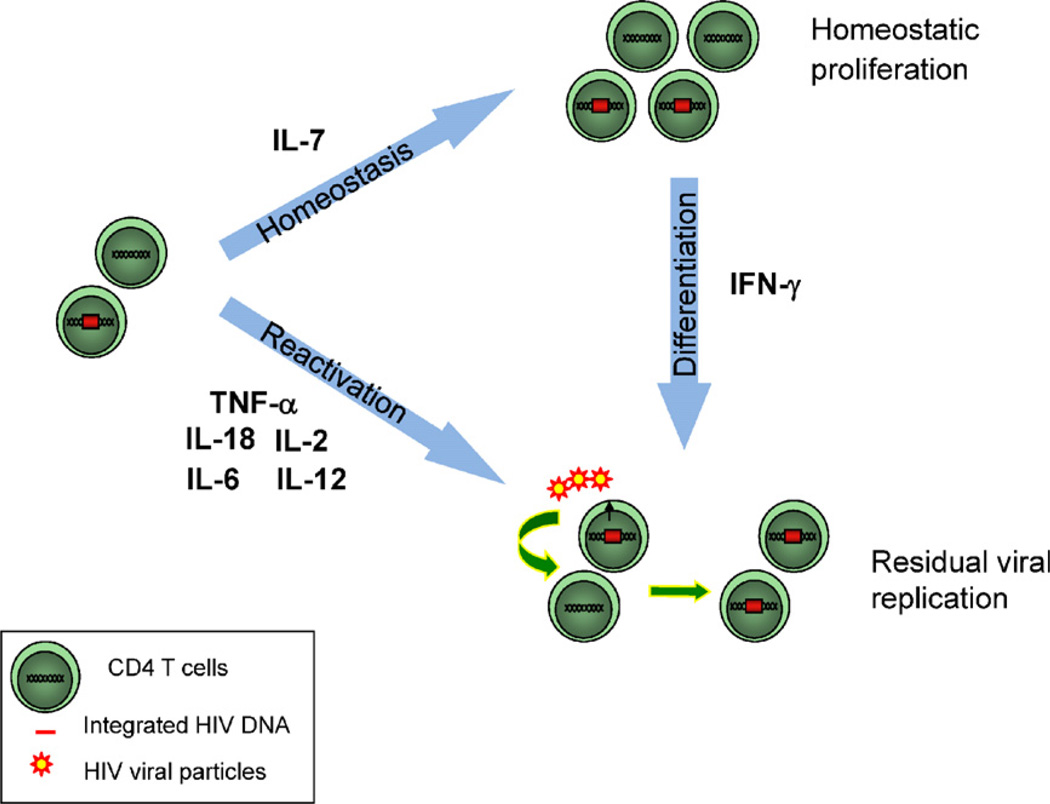
Fig. 2.
Role of cytokines in HIV persistence. IL-7 plays an important role in the homeostasis of CD4+ T cells and may ensure the long-term persistence of latently infected cells through homeostatic proliferation during HAART. Several cytokines expressed at high levels in the plasma and lymphoid tissues of HIV infected subjects such as TNF-α, IL-2, IL-12 and IL-18 may induce HIV reactivation from latently infected cells and sustain ongoing viral replication during HAART. As a potent pro-differentiation agent, IFN-γ may induce viral production in latently infected cells concomitant to cell-differentiation. In addition, by generating more targets for HIV infection, IFN-γ may in turn enhance viral replication.