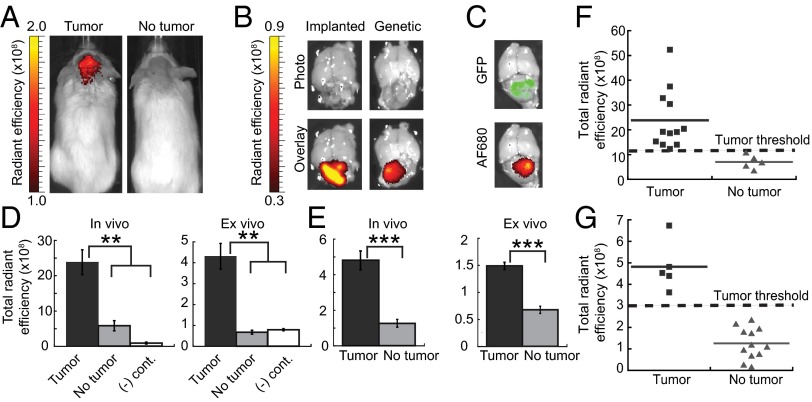
Fig. 2.
AF680–EETI 2.5F illuminates mouse medulloblastoma in vivo and ex vivo. (A) Ptch+/− mouse with a tumor (Left) and mouse with no tumor (Right) imaged 2 h after tail vein injection of AF680–EETI 2.5F. (B) Knottin peptide bound specifically to tumor tissue in orthotopic Med1-MB or Ptch+/− genetic models as confirmed by ex vivo imaging of excised brain tissue. (C) Ptch+/−; Math1-GFP mouse, which produces GFP-labeled tumor cells, showed colocalization of GFP signal and knottin AF680 signal. Quantification of in vivo and ex vivo total fluorescent signal 2 h postinjection discriminated between tumor-bearing and non–tumor-bearing mice for implanted Med1-MB (D) and Ptch+/− (E) tumors. AF680–EETI RDG [(-) cont., negative control] generated low imaging signals (D), confirming the integrin-targeting specificity of AF680–EETI 2.5F. Values are reported as the mean ± SE (**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). (F and G) Plots of in vivo transcranial AF680 signals for individual mice. Defined signal thresholds (dashed lines) clearly delineate mice with tumors from mice without tumors for orthotopic Med1-MB (F) and genetic Ptch+/− (G) models.