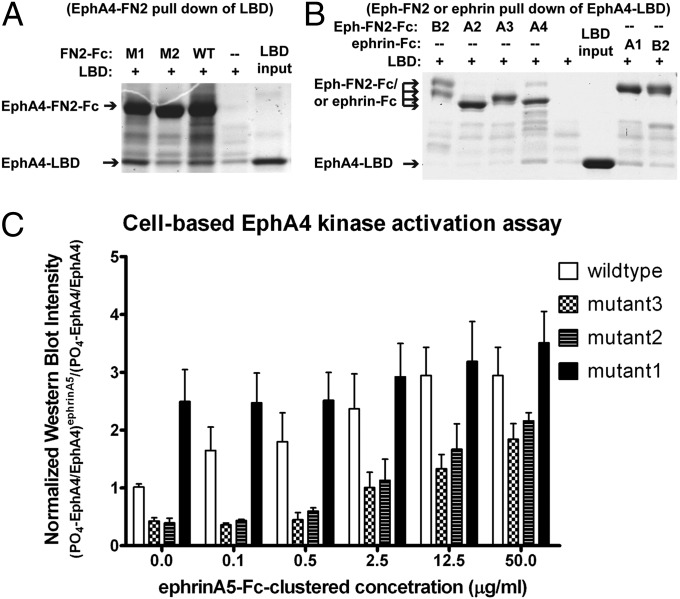
Fig. 4.
Mutations in the EphA4 preclustering interface functionally affect forward signaling. The effects of various mutations in the EphA4 preclustering interface were evaluated in pull-down and kinase activation assays. Mutants M3 and M2 (E238A and R454A/Y455A, respectively) weaken the interface, whereas mutant M1 (N504D/T507D) strengthens the interface. (A) Pull-down assay between LBD and mutant FN2 of EphA4: The Fc-tagged EphA4 FN2 domains with mutations that were designed to either enhance (M1) or weaken (M2) the preclustering interface were used to pull down the EphA4 LBD. WT EphA4 FN2 was used as positive control. The M1 FN2 binds to the LBD better than WT, whereas the M2 FN2 binding is weaker than WT. (B) EphA4 LBD binding to FN2 domains of different Ephs and to ephrins: The EphA4-LBD was tested in a pull-down assay with Fc-tagged FN2 of different Eph family members as labeled above lanes 1–4. EphA4 LBD binds only the EphA4 FN2. Fc-tagged ephrin-A1 and ephrin-B2 were used as positive control (lanes 7–8), confirming that ephrin-A1 binds EphA4 better than ephrin-B2. (C) Cell-based EphA4 kinase activation assay: HEK293 cells stably expressing WT or mutant full-length EphA4 were treated with increasing concentrations of ephrin-A5-Fc for 10 min and harvested. The activated (phosphorylated) EphA4 in the cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody and was then detected with an anti-EphA4 antibody in Western blots. The Western blot films were scanned, and the signal intensity was quantified and plotted. The amount of phosphorylated EphA4 was normalized for the total EphA4 amount in the total cell lysates. All intensity readings were calculated as the ratio to the basal (ligand-independent, resting) EphA4 phosphorylation level. The experiments were performed in triplicate, and the error bars are shown in the plot.