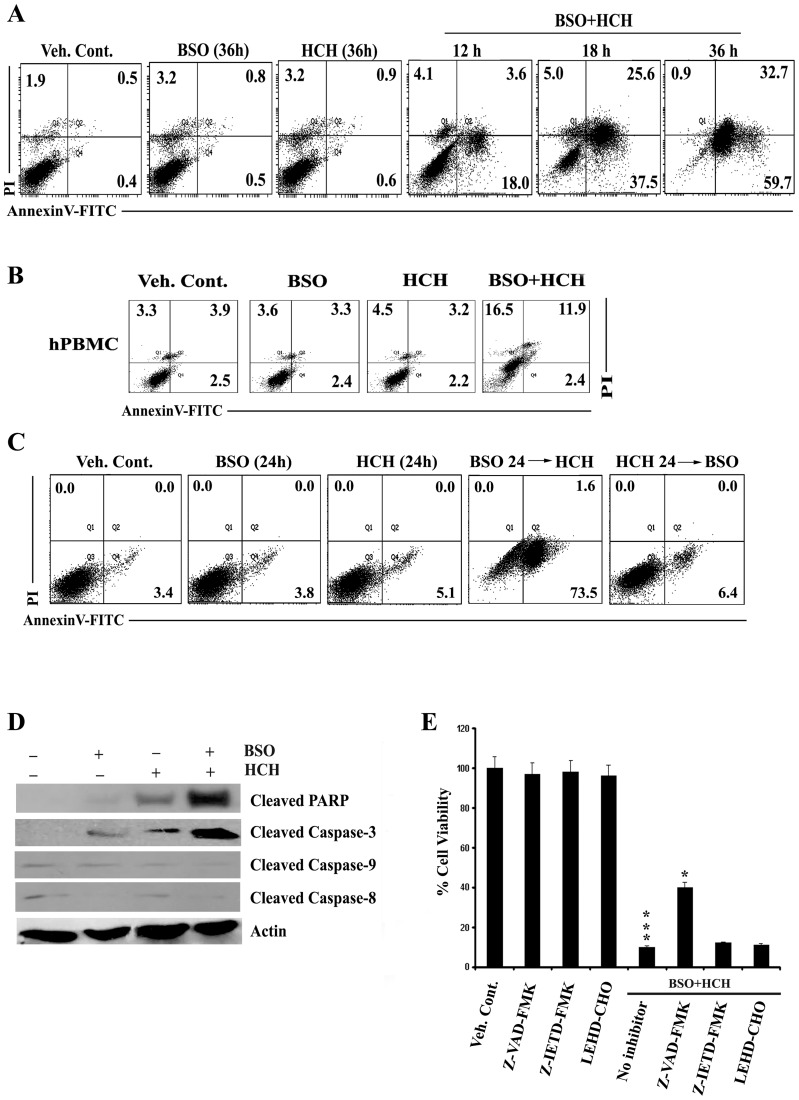
Figure 2. Sequential administration of BSO potentiates HCH- induced apoptosis in caspase dependent manner.
(A) K562 cells were treated with 100 µM BSO and 10 µM HCH either alone or in combination for indicated times and apoptosis was measured by annexin V/PI binding assay. Dot plots are representative of two similar experiments. (B) hPBMC were treated as indicated for 36 h and apoptosis was measured by annexin V/PI binding assay. Representative of two similar experiments. (C) BSO (100 µM) was administered 24 h prior addition of HCH (10 µM) and vice versa in K562 cells and incubated for 24 h for measurement of apoptosis by annexin V/PI binding assay. Representative of two similar experiments. (D) K562 cells were incubated with 100 µM BSO and 10 µM HCH or their combination for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were subjected to western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. Antibody to actin was used as loading control. (E) K562 cells were pre-treated with pan-caspase inhibitor Z-VAD-FMK (50 µM), caspase 8 inhibitor Z-IETD-FMK (50 µM) and caspase-9 inhibitor LEHD-CHO (25 µM) before treatment with BSO (100 µM) and HCH (10 µM). After 36 hours, cell viability was assessed using MTT assay. Every column represents mean ± SD of three experiments. *** p<0.001 compared to treatment with vehicle control; * p<0.05 compared to treatment with no caspase inhibitors.