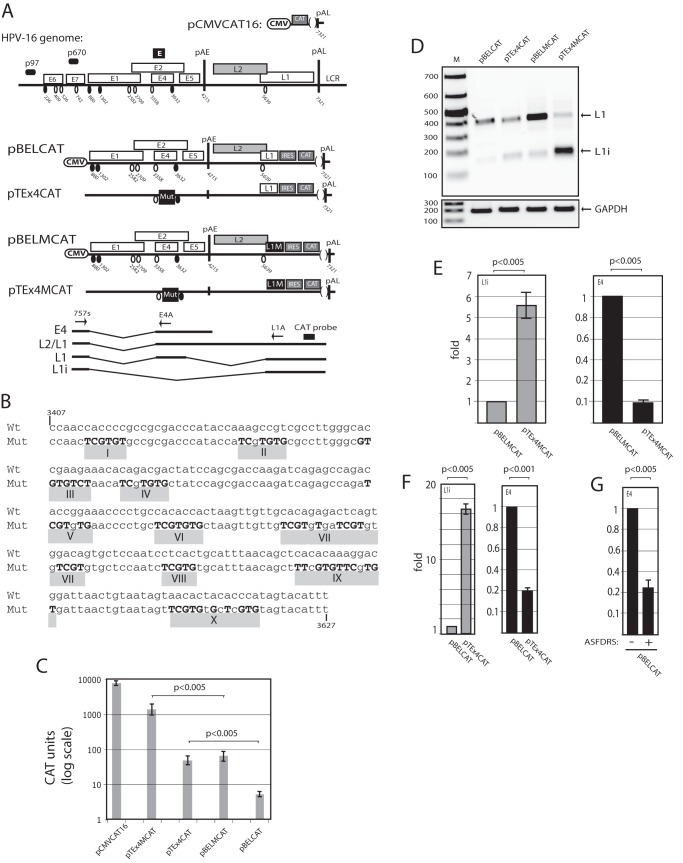
Figure 1. Characterisation of the splicing enhancer downstream of HPV-16 3′-splice site SA3358 using novel HPV-16 reporter plasmids.
(A). Schematic representation of the HPV-16 genome, the subgenomic HPV-16 expression plasmids and the control plasmid pCMVCAT16 [39]. The early and late viral promoters p97 and p670 are indicated. Numbers indicate nucleotide positions of 5′- (filled circles) and 3′-splice sites (open circles) or the early and late poly (A) sites pAE and pAL, respectively, and the borders of deletions. L1M represents a previously described mutant HPV-16 L1 sequence in which a number of nucleotide substitutions that inactivate splicing silencers have been inserted downstream of SA5639. IRES, the poliovirus internal ribosome entry site sequence; CAT, CAT reporter gene; CMV, human cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter; LCR, long control region. mRNAs produced by the plasmids are indicated. The position of the CAT probe and RT-PCR primers (arrows) are indicated. (B) The HPV-16 sequence between nucleotides 3407 and 3627 in the exon between SA3358 and SD3632 is displayed.The previously identified 10 clusters of 15 ASF/SF2 bind sites [18] predicted by ESE finder [43]. (C) CAT protein levels produced in transfected cells. CAT was monitored as described in Materials and Methods. Mean values and standard deviations are shown. Note the logarithmic scale. (D) RT-PCR with primers 757s and L1A on cDNA of cytoplasmic RNA extracted from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids.L1 and L1i mRNAs are indicated. The RT-PCR is qualitative only, as it has not been optimised for RNA quantitation. M, molecular weight marker; GAPDH,cDNA amplified as internal control. (E, F) Real time PCR of HPV-16 E4 mRNAs using primers 757s and E4A and L1i mRNAs with primers 757s and L1A from as described in Materials and Methods. (G) Real time PCR of HPV-16 E4 mRNAsproduced from pBELCAT in the absence of presence of cotransfectedpASFDRS plasmid. RT-PCR primers were 757s and E4A.