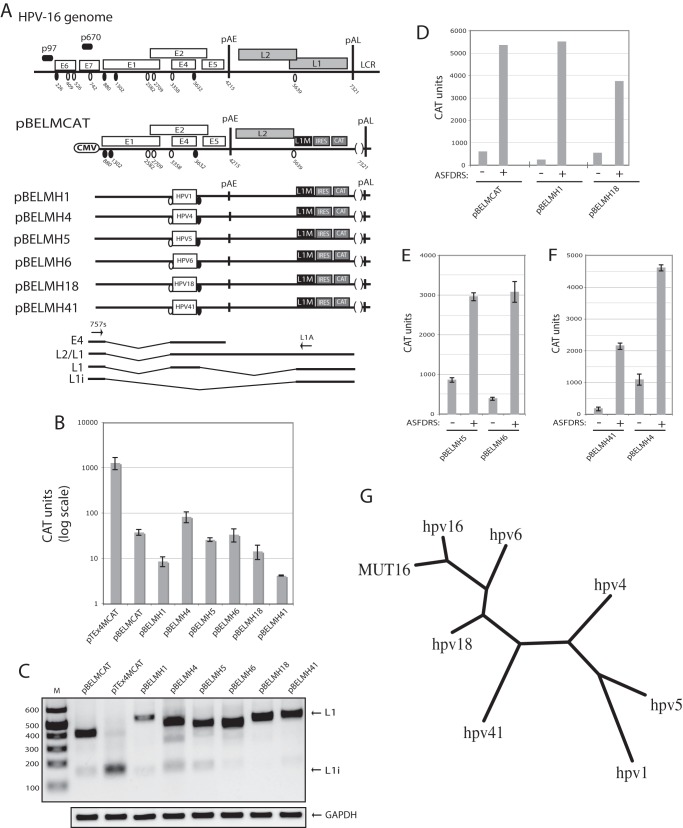
Figure 2. Location of a splicing enhancer in the HPV E2/E4 coding region is conserved among HPVs.
(A). Schematic representation of the HPV-16 genome, the subgenomic HPV-16 expression plasmids and the control plasmid pCMVCAT16 [39]. The early and late viral promoters p97 and p670 are indicated. Numbers indicate nucleotide positions of 5′- (filled circles) and 3′-splice sites (open circles) or the early and late poly (A) sites pAE and pAL, respectively, and the borders of deletions. L1M represents a previously described mutant HPV-16 L1 sequence in which a number of nucleotide substitutions that inactivate splicing silencers have been inserted downstream of SA5639. Boxes indicate position of various HPV sequences inserted between nucleotide positions 3407 and 3627 in HPV-16 plasmid pBELMCAT [38]. IRES, the poliovirus internal ribosome entry site sequence; CAT, CAT reporter gene; CMV, human cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter; LCR, long control region. mRNAs produced by the plasmids are indicated. The positions of the RT-PCR primers (arrows) are indicated. (B) CAT protein levels produced in HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. CAT was monitored as described in Materials and Methods. Mean values and standard deviations are shown. Note the logarithmic scale. (C) RT-PCR with primers 757s and L1A on cDNA of cytoplasmic RNA extracted from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. L1 and L1i mRNAs are indicated. M, molecular weight marker; GAPDH, cDNA amplified as internal control. (D, E, F) CAT protein levels produced in HeLa cells transfected with the indicated HPV plasmids in the presence or absence of ASFDRS expression plasmid [18]. CAT was monitored as described in Materials and Methods. Mean values and standard deviations are shown. Note that results in D and E are from transfections of cells in 24-well plates, whereas results in B and C are from 60 mm plates. (G) Phylogenetic tree of exonic sequences located between the splice sites that correspond to HPV-16 SA3358 and SD3632 of various HPV types. MUT16 represents the mutated HPV-16 sequence shown in Figure 1B.