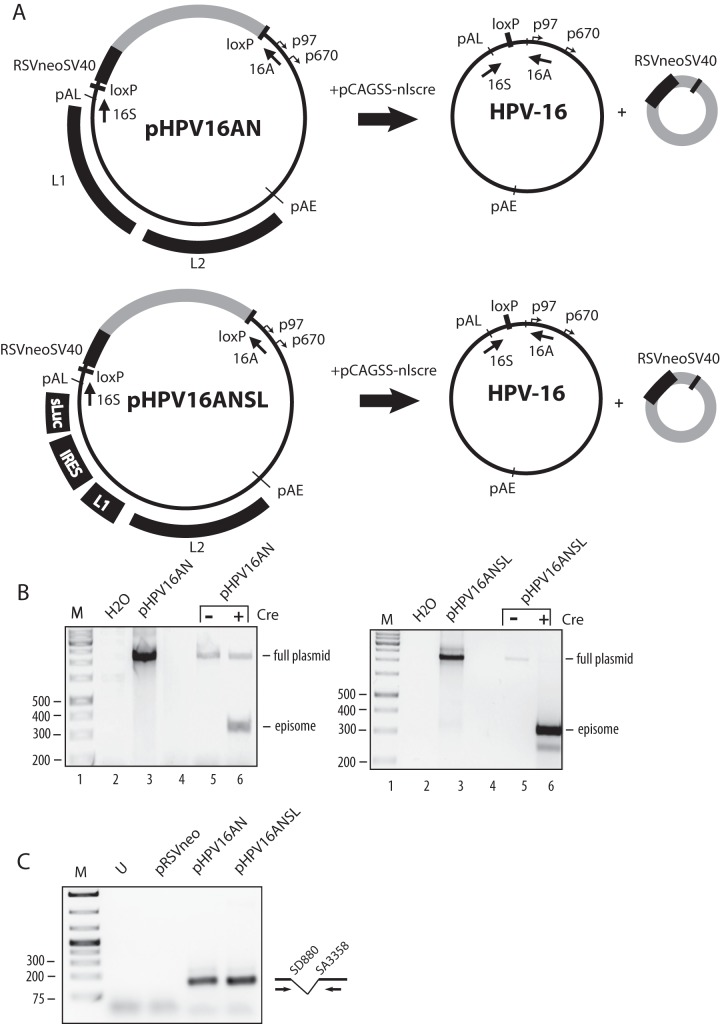
Figure 7. Generation of HPV-16 genomes with the secreted luciferase gene in place of L1.
(A). Structures of genomic HPV-16 plasmids pHPV16AN and pHPV16ANSL. LoxP sites and HPV-16 early (p97) and late (p670) promoters are indicated. Arrows denote positions of PCR primers 16S and 16A. The casette encoding the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat promoter driving the neomycin resistance gene, followed by the simian virus 40 polyA signal is indicated. The effect of the crerecombinase on these plasmids is illustrated. pAE and pAL, HPV-16 early and late polyA signals, respectively; L1 and L2, late HPV-16 genes L1 and L2; sLuc, secreted luciferase; IRES, poliovirus 2A internal ribosome entry site. (B) PCR with primers 16S and 16A on total DNA extracted from human primary keratinocytes transfected with pHPV16AN or pHPV16ANSL in the absence or presence of the cre-expressing plasmid pCAGGS-nlscre (lanes 5 and 6) [37]. Primers 16S and 16A are located on each side of the LoxP sites in pHPV16AN and pHPV16ANSL and the PCR-reaction yields a 366-nucleotide PCR fragment that is diagnostic for recombination at the LoxP sites. A larger band is amplified from plasmid DNA that has not recombined (lane 3). A negative control is shown in lane 2. M, molecular size marker. (C) Nested RT-PCR on total RNA extracted from cells transfected with pHPV16AN, pHPV16ANsl or pRSVneo in the presence of pCAGGS-nlscre [37]. Primers 757s and E4A detect early HPV-16 mRNAs spliced from SD880 to SA3358 (E4), the most common early HPV mRNA. U, nested RT-PCR on RNA from untransfected cells; M, molecular size marker.