Figure 1. Pathophysiological framework of HCM.
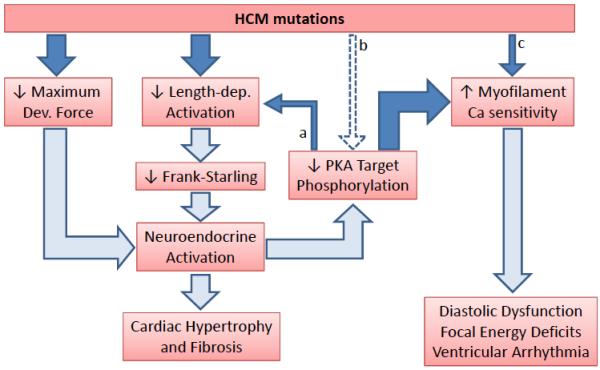
Solid arrows indicate experimental findings reported by Sequeira and coworkers. Open arrows indicate the consequences based on experimental evidence from other studies. (a) Impaired length-dependent activation can also be caused by PKA hypophosphorylation (i.e., of TnI). (b) HCM mutations may directly interfere with phosphorylation of myofilament PKA targets. (c) Only a subset of HCM mutations directly alter myofilament Ca sensitivity.
