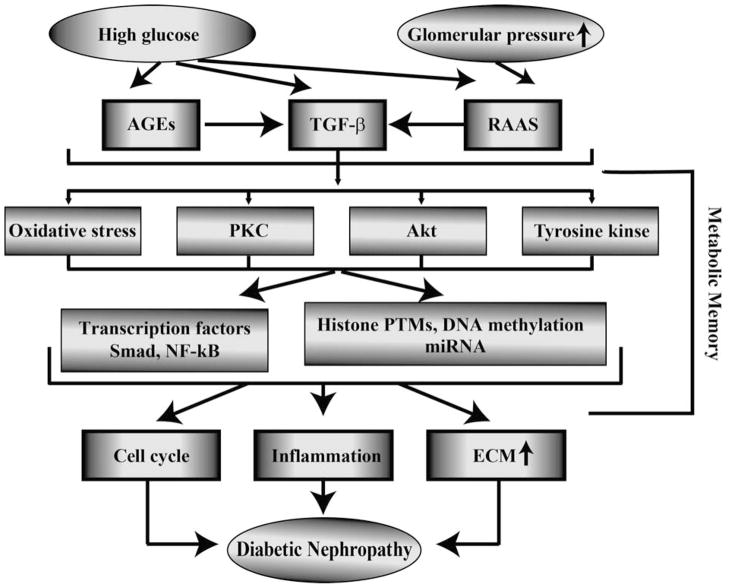
Figure 1. Major pathways involved in the pathophysiology of diabetic nephropathy.
Complex interactions between metabolic and hemodynamic factors regulate the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Persistence of HG mediated damage including epigenetic modifications even after return to normoglycemia can lead to metabolic memory and increased risk for long term complications. TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; AGEs, advanced glycation end product; RAAS, rennin angiotensin aldosterone system; PKC, protein kinase C; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; PTMs, posttranslational modifications; ECM, extracellular matrix.