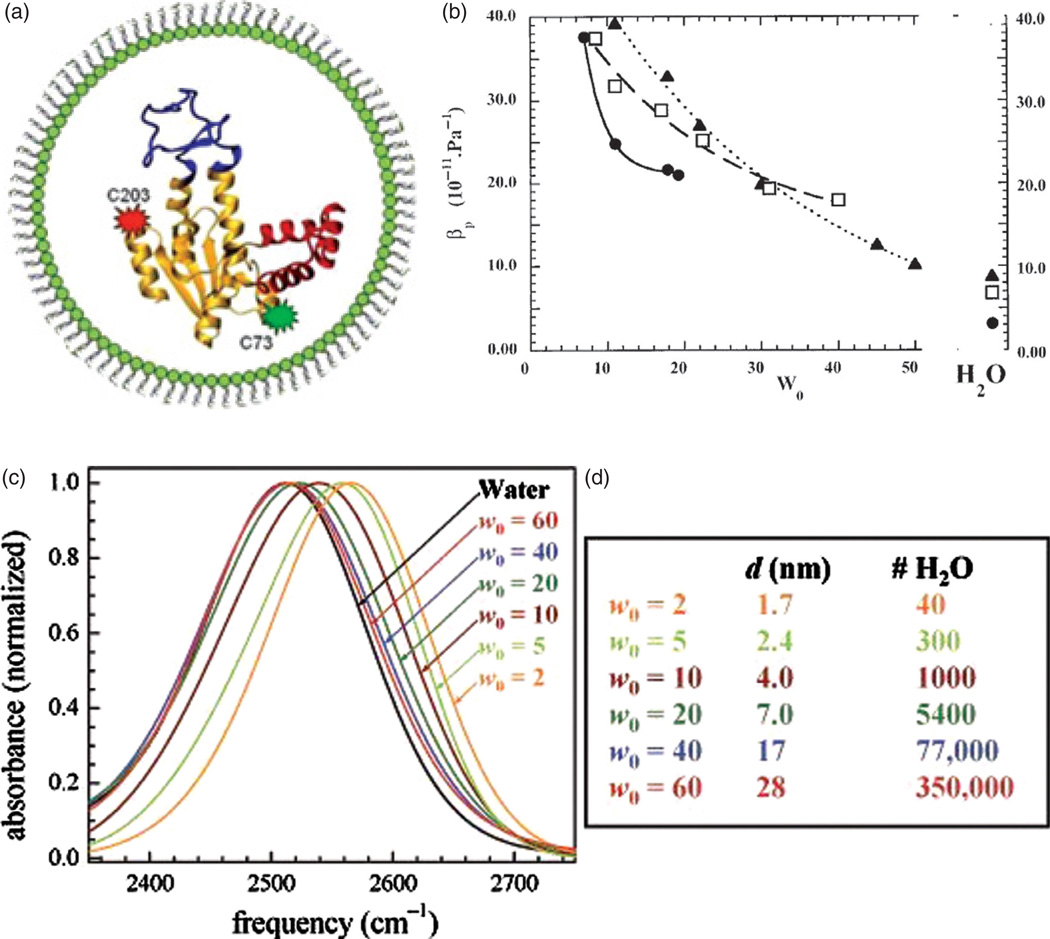
Figure 21.
(a) A protein inside of a reverse micelle; (b) an empirically derived plot of the adiabatic compressibility of cytochrome c, lysozyme and lactoglobulin, indicative of the dimensions and tertiary structure of the protein, as a function of parameterwthe molar ratio between the amount of water and the amount of surfactant in the microemulsion, directly proportional to the size of reverse micelle; (c) a blue shift in the absorbance of water in the microwave range induced by a decrease in the size of nanoscopic water pools of reverse micelles, along with (d) the number of water molecules in reverse micelles of the given size. Reprinted with permission from [206], D. Valdez, et al., Hydration and protein folding in water and in reverse micelles: compressibility and volume changes. Biophys. J. 80, 2751 (2001). © 2001, Elsevier; From [207], D. E. Moilanen, et al., Confinement or properties of the interface? dynamics of nanoscopic water in reverse micelles, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 14311 (2007). © 2007, American Chemical Society.