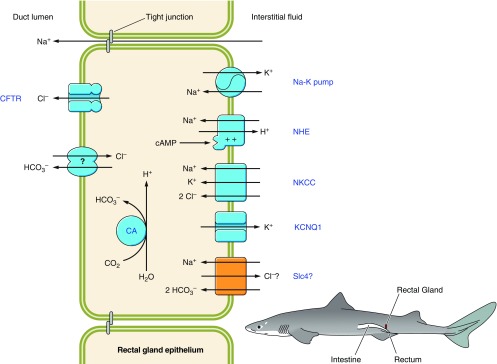
Figure 11.
Role of an NCBT in the rectal gland of cartilaginous fish. The rectal gland duct joins the intestine at a point upstream of the rectum (see cartoon dogfish). In rectal gland epithelia, the Na-K pump maintains a low intracellular [Na+] driving basolateral Na/K/Cl cotransporter (NKCC) activity that supplies Cl− for secretion across the apical membrane by CFTR. Anion secretion draws Na+ and H2O through a paracellular pathway, resulting in the secretion of a NaCl-rich solution from the interstitial fluid/blood. CO2 accumulation is dissipated by intracellular carbonic anhydrase (CA). Respiratory acidosis is prevented by NHE and NCBT action. NHE and NCBT could also support HCO3− secretion via the unidentified apical anion exchanger, that is likely a member of the Slc26 family (84). KCNQ1 is a voltage-sensitive K+ channel (1018), also known as Kv7.1.