Figure 6.
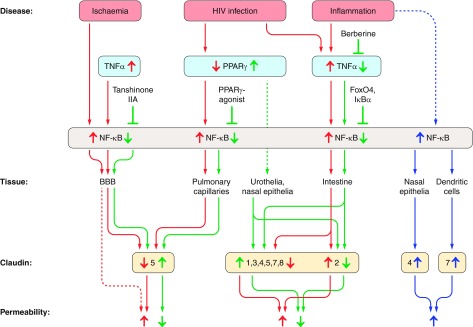
Summary of NF-κB-mediated TNF-α and PPAR-γ effects on claudin expression and epithelial permeability. In most epithelia, increases in NF-κB cause an increase in epithelial permeability, due to decreased expression in tightening tight junction proteins and/or increased expression in pore-forming claudin-2 (red arrows). Direct or indirect inhibition of NF-κB causes opposite effects (green arrows). In a few, exceptional cases, NF-κB was observed to upregulate tightening claudins, causing decreases in epithelial permeability (blue arrows). Figure is based on References 9, 22, 40, 41, 81, 120, 174, 210, 234, 237, 274, 335, 347, 378, 379, 384, 426. See text for detailed description.
