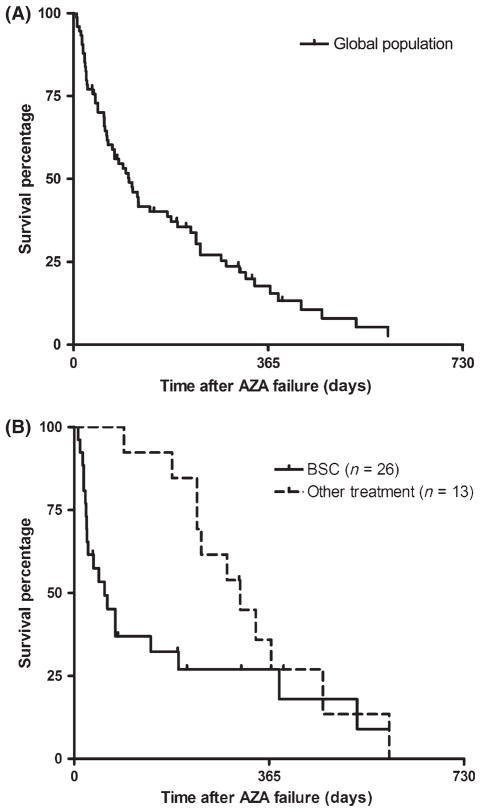
Fig 1.
(A) Kaplan Meier estimates of the overall survival after azacitidine (AZA) failure for secondary acute myeloid leukaemia. (B) Survival analysis according to the salvage treatment regimen. The curves represent the survival estimates for the cohort of patients. Each tick mark represents a censored patient. Overall response rate for each treatment group is presented with the number of patients evaluable for response in each cohort. Best supportive care (BSC) included palliative chemotherapy; other treatments included allogeneic transplantation, epigenetic-targeted agents and intensive ‘acute myeloid leukaemia-like’ chemotherapy regimens.