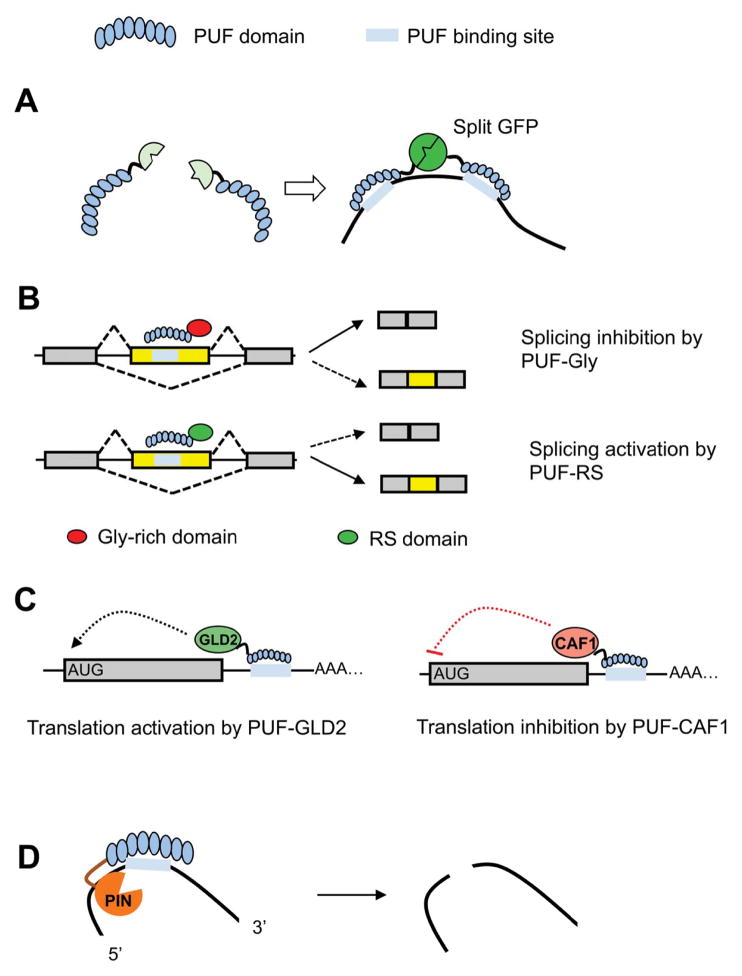
Fig. 2.
Engineered PUF factors. A. Fluorescent probe for in vivo RNA labeling. Combination of split GFP (or other fluorescent protein) with PUF scaffold generated an RNA probe to visualize RNA in live cells. B. Engineered splicing factors. Combination of a PUF scaffold with an RS domain or a Gly-rich domain generated splicing factors that activate or inhibit splicing of alternative exon. C. Modulation of translation. Fusion of GLD2 or CAF1 with PUF domain produced novel factors that can activate or inhibit mRNA translation. D. Artificial site-specific RNA endonuclease. Combination of PUF domain with a non-specific RNA endonuclease (PIN domain) can produce a new class of enzymes that specifically recognize and cleave RNA.