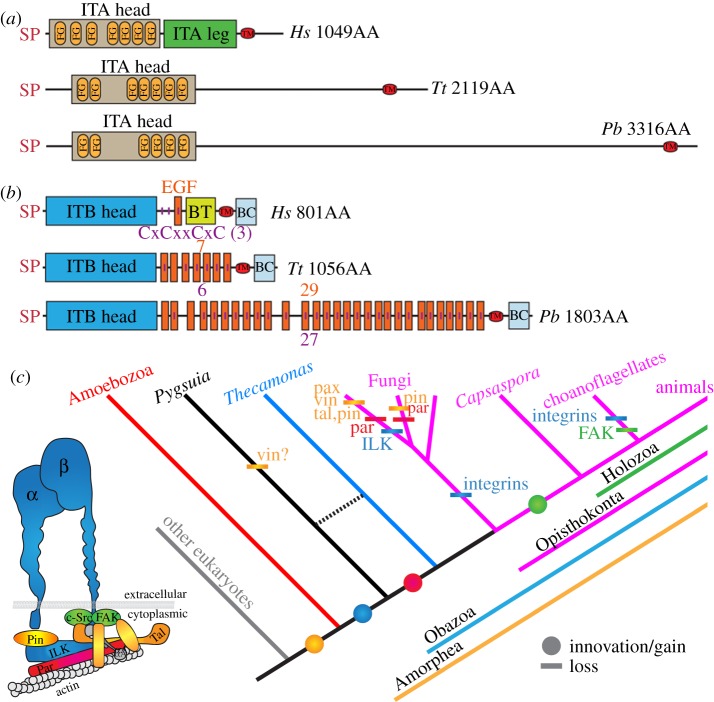
Figure 4.
(a) Domain architecture of ITA from P. biforma (Pb) compared to a canonical ITA of Homo sapiens (Hs) (ITGA5, GenBank NP_002196) and the ITA in Thecamonas trahens (Tt) [26]. (b) Domain architecture of ITB of Pb compared to a canonical ITB of Hs (ITGB1, GenBank NP_391988) and the ITB in Tt [26]. SP, signal peptide (SignalP-NN(euk)); ITA head, integrin α, β-propeller (IPR013519); FG, FG-gap (PS51470); ITA leg, integrin α-2 (IPR013649); TM, transmembrane domain; ITB head, integrin β chain (PF00362); EGF, epidermal growth factor; extracellular (IPR013111); BT, integrin-B tail (PF07965); BC, integrin-B cytoplasmic region (PF08725). Vertical purple lines represent cysteine-rich repeats (CxCxxCxC) (PS00243). The number of EGF and CxCxxCxC are indicated. (c) Phylogenetic distribution of IMAC. The inset depicts IMAC coloured in accordance with the distributions shown in the tree. Circle, innovation/gain; bar, loss. Abbreviations: vin, vinculin; pax, paxillin; tal, talin; par, parvin; pin, particularly interesting new cysteine-histidine-rich protein; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; ILK, integrin-linked kinase; αA, alpha-actinin; α, α-integrin; β, β-integrin; IP, Interpro; PF, Pfam; PS, ProSite.