Figure 2.
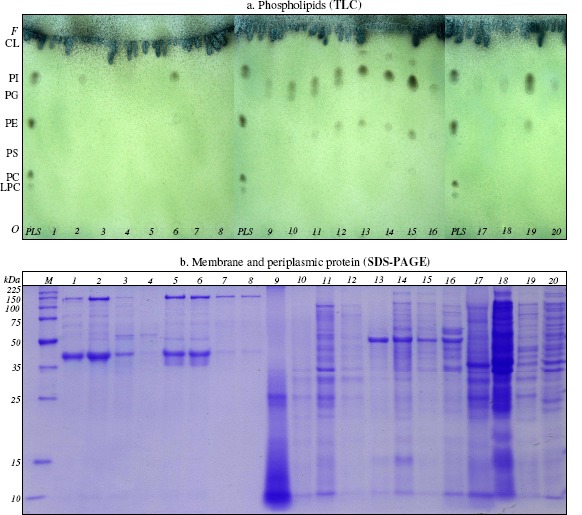
The lipid profile (a.) and protein profile (b.) modifications of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in the presence of mixture of saturated (n-hexane, n-hexadecane, cyclohexane), monoaromatic (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene) and polyaromatic (naphthalene, 2-methylnaphthalene, fluorene) hydrocarbons Oerskovia sp. IBBPo2 (lanes 1-4), Corynebacterium sp. IBBPo3 (lanes 5-8), Chryseomonas sp. IBBPo7 (lanes 9-12), Pseudomonas sp. IBBPo10 (lanes 13-16), Burkholderia sp. IBBPo12 (lanes 17-20); bacterial strains cultivated onto liquid LB-Mg medium without hydrocarbons (lanes 1, 5, 9, 13, 17); bacterial strains cultivated onto liquid LB-Mg medium with: mixture of saturated hydrocarbons (lanes 2, 6, 10, 14, 18), mixture of monoaromatic (lanes 3, 7, 11, 15, 19), and mixture of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (lanes 4, 8, 12, 16, 20). Panel a. Phospholipids standards, Sigma-Aldrich, Supelco (lane PLS); origin (O), solvent front (F), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylinositol (PI), cardiolipin (CL). Panel b. Broad range protein molecular weight marker, Promega (lane M).
