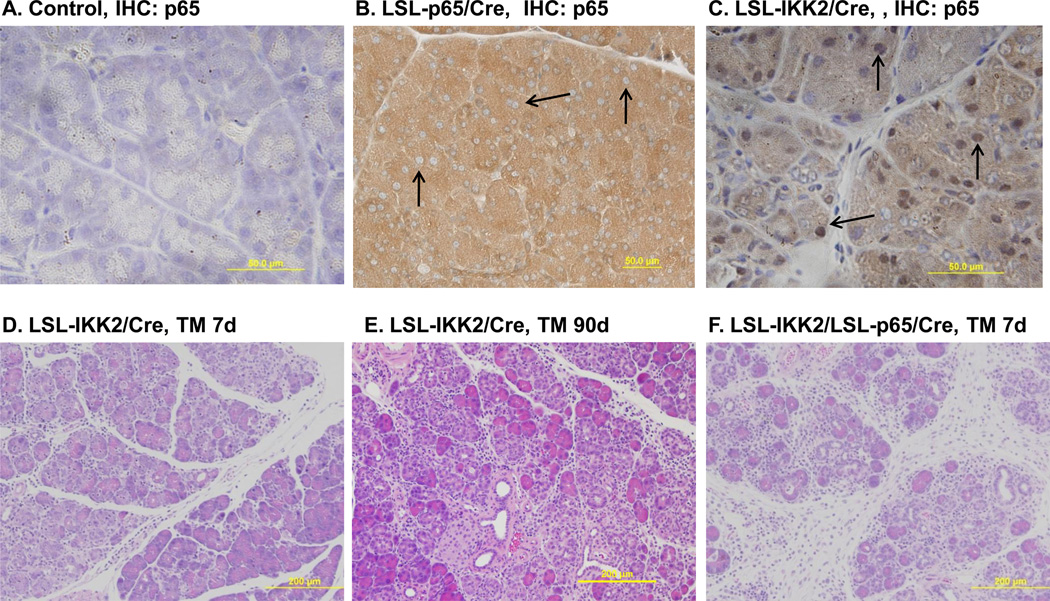
Figure 5.
Acinar specific expression of constitutively active IKK2 led to NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation and pancreatitis. A. Immunohistochemical staining with antibody against p65 did not detect p65 nuclear translocation in control mice. B. Transgenic p65 expression in Ela-CreERT × LSL-p65 (LSL-p65/Cre) mice led to higher basal p65 level (brown) without nuclear translocation (arrow). C. Pancreatic specific expression of constitutively active IKK2 in Ela-CreERT × LSLIKK2 (LSL-IKK2/Cre) mice caused p65 nuclear translocation (arrow). D. Pancreatic acinar damage and inflammatory cell infiltration were obvious seven day after TM induction of IKK2 expression. E. Pancreatic acinar damage, inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrosis were evident 3 months after TM induction of IKK2 expression. E. Co-expression of IKK2 and p65 further increased the severity of pancreatitis in Ela-CreERT × LSL-IKK2 × LSL-p65 (LSL-IKK2/LSL-p65/Cre) mice (7 days after TM).