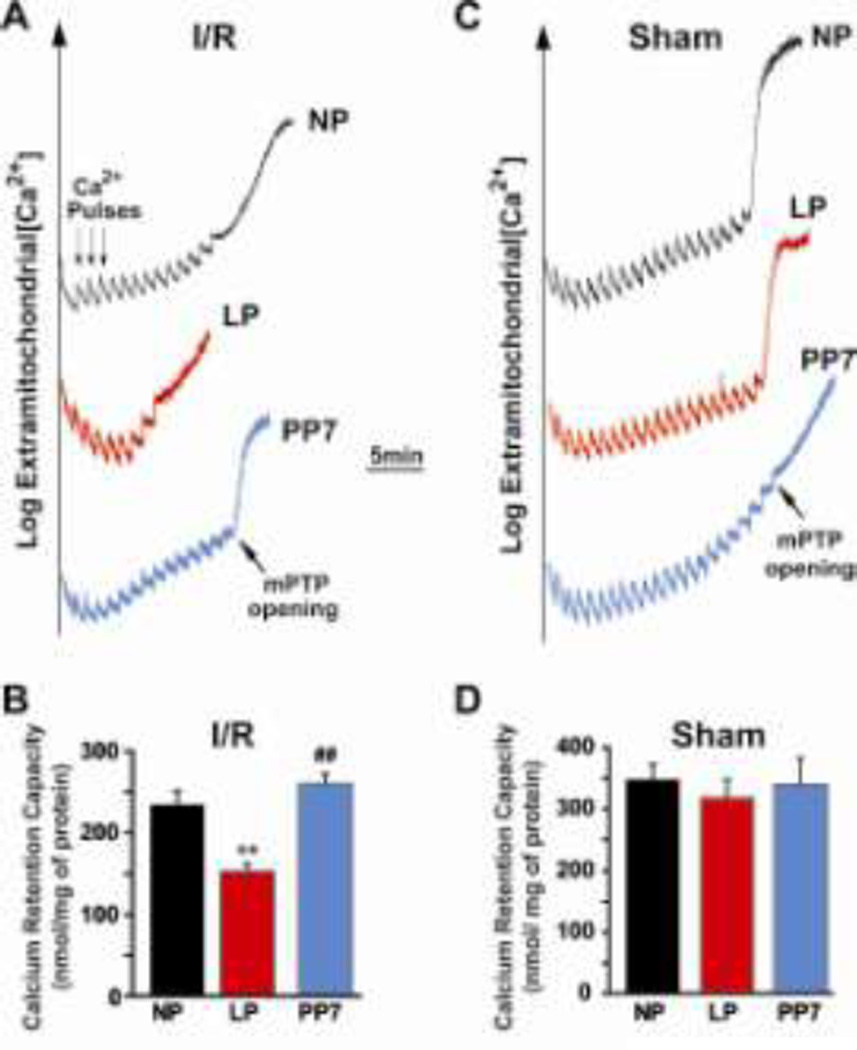
Fig. 5. Lower threshold for triggering mPTP opening in response to calcium overload in LP compared to NP and PP7.
A. Typical recordings of the mPTP opening in isolated mitochondria from NP, LP and PP7 groups subjected to 20min of global ischemia followed by 10min of reperfusion. Twelve pulses (arrows) of 20 nmol calcium were required to trigger the opening of mPTP in NP compared to 7 pulses in LP and 14 pulses in PP7. B. Calcium retention capacity (CRC) in NP (white bar), LP (black bar) and PP7 (gray bar) subjected to ischemia/reperfusion injury. C. Typical recordings of the mPTP opening in isolated mitochondria from NP, LP and PP7 groups not subjected to ischemia/reperfusion injury. D. Calcium retention capacity (CRC) in NP (white bar), LP (black bar) and PP7 (gray bar) in mice not subjected to ischemia/reperfusion injury, **p <0.01 LP vs. NP; ##p<0.01 PP7 vs. LP; p >0.05 NP vs. PP7(n=6).