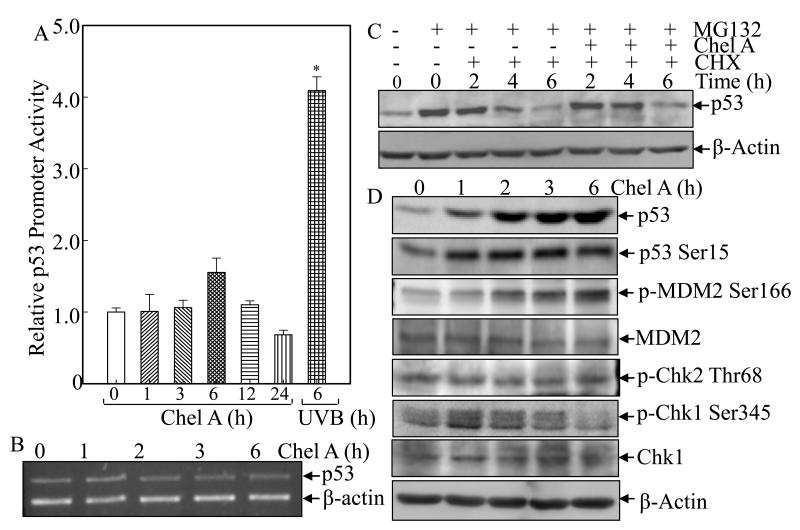
Fig. 3. Chel A induces p53 protein expression by inhibiting p53 protein degradation.
(A) Cl41 cells stably transfected with p53 promoter-driven luciferase reporter were exposed to Chel A for indicated time periods or to UVB as positive control. The luciferase activity was determined and the results were presented as relative p53 promoter activity. The symbol (*) indicates a significant increase as compared with that of medium control (p<0.05). Each bar indicates the mean and standard deviation of three independent experiments. (B) Cl41 cells were exposed to Chel A for indicated time periods, and p53 mRNA was determined by RT-PCR. (C) Cl41 cells were treated with MG132 for 4 h, followed by exposure with CHX combined with Chel A or CHX alone as indicated. Then cell extracts were subjected to Western Blotting and β-Actin protein expression was used as a protein loading controls. (D) Cl41 cells were exposed to Chel A for indicated time periods, and cell extracts were subjected to Western Blotting and β-Actin protein expression was used as a protein loading controls.