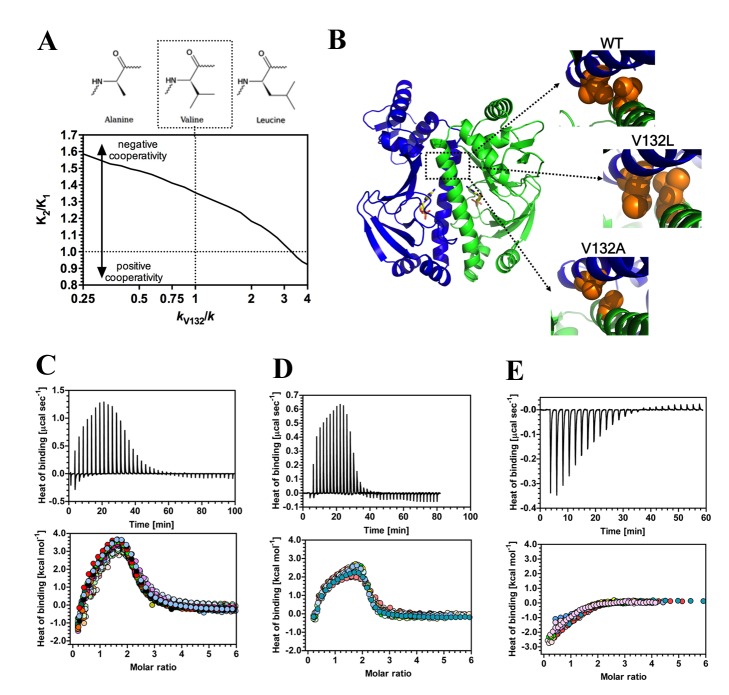
Figure 2. The influence of third-site mutations on allostery in CAP.
(A) Predicted influence of mutation of V132 on allostery in CAP. The chart represents the ratio of the second to first dissociation constants for cAMP (K 2/K 1) plotted against spring constant at V132 (k V132/k). The structures are the proposed corresponding mutations. (B) Close-up of the X-ray crystal structures for CAP variants showing the hydrophobic interaction surface at amino acid 132 in wild-type, V132L, and V132A proteins. (C–E) ITC traces (upper panel) and binding isotherms (lower panel; the different coloured symbols represent individual experiments) for the calorimetric titration of cAMP to CAP wild-type (C), V132L (D), or V132A (E). The thermodynamic parameters obtained are summarized in Tables 1 and S2.