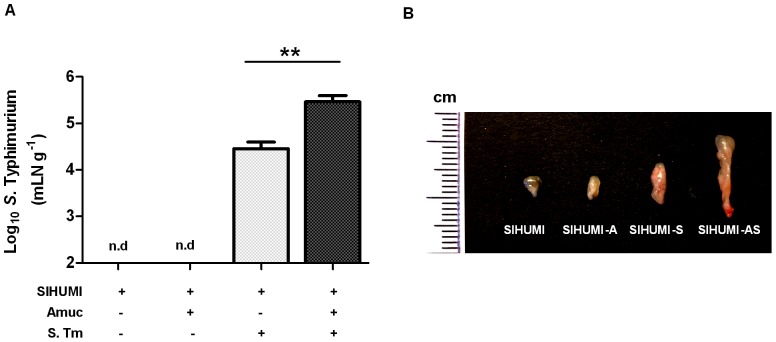
Figure 5. SIHUMI mice colonized with both A. muciniphila and S. Typhimurium display enlarged mLN and elevated S. Typhimurium cell numbers.
(A) Mesenteric lymph nodes (mLN) were obtained from four groups of gnotobiotic C3H mice. SIHUMI mice were subsequently inoculated with A. muciniphila or S. Typhimurium or consecutively with both organisms (see Figure 1). The mLN tissue was homogenized and DNA was isolated to quantify S. Typhimurium using quantitative PCR with primers targeting the ttr-region of S. Typhimurium. Absolute cell numbers were calculated based on calibration curves with known concentrations of S. Typhimurium. The mLN of SIHUMI-AS mice contained 10-fold higher cell numbers of S. Typhimurium compared to SIHUMI-S mice. Data are expressed as mean±standard error. n = 10 mice per group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. n.d: not detected. Amuc: A. muciniphila; S. Tm: S. Typhimurium. (B) The photograph shows four lymph nodes, each representative of one of the four mouse groups and a cm scale. Twelve week old gnotobiotic SIHUMI mice with both A. muciniphila and S. Typhimurium displayed an increased size of their mesenteric lymph nodes compared to SIHUMI mice infected with S. Typhimurium only.