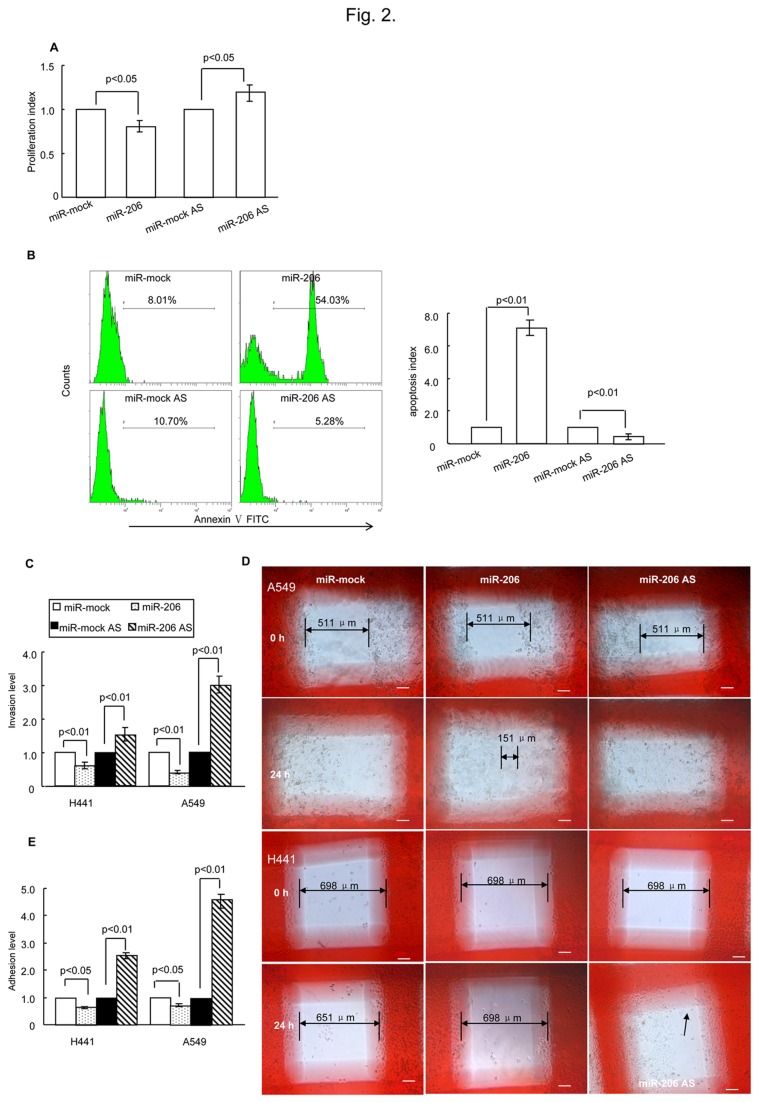
Figure 2. miR-206 affected cell biological functions.
(A) miR-206 had a significant effect on cell proliferation as analyzed using XTT (2-3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-5-[(phenylamino) carbonyl]-2H-tetrazolium hydroxide) 24 h after transfection. (B) miR-206 was involved in cell apoptosis as assessed by flow cytometry. H441 cells were treated with miRNA and apoptosis inducers was described in Methods. Twenty-four hours later, the cells were collected and analyzed. Profiles on the left are representative of at least three independent experiments. Statistical analysis is shown on the right. (C) Determination of miR-206 involvement in cell invasion by the transwell invasion assay. The relative number of miR-206-trasfected cells (A549 and H441) that migrated compared with miR-mock-transfected cells, and the relative number of miR-206 AS-trasfected cells that migrated compared with mock AS-trasfected cells after 24 h post-transfection. (D) The wound healing assay showed that after 24 h in culture, in A549 cells, the mock group and the miR-206 AS group had covered the artificial wound field, whereas the miR-206 group still had a blank area (double arrowed, length: 151 µm). As for H441 cells, the miR-206 AS group covered the artificial wound field (arrowed), and the mock group and the miR-206 group left the original wound field open (double arrowed, mock length: 651µm, miR-206 length: 698 µm). White bars represent 100 µm. (E) Cell-cell adhesion abilities were determined by an adhesion assay. The relative number of adhesion cells (A549 and H441) after miR-206 transfection compared with cells transfected with miR-mock, and the relative number of adherent cells after miR-206 AS transfection compared with mock AS-transfected cells after 24 h post-transfection. AS, antisense.