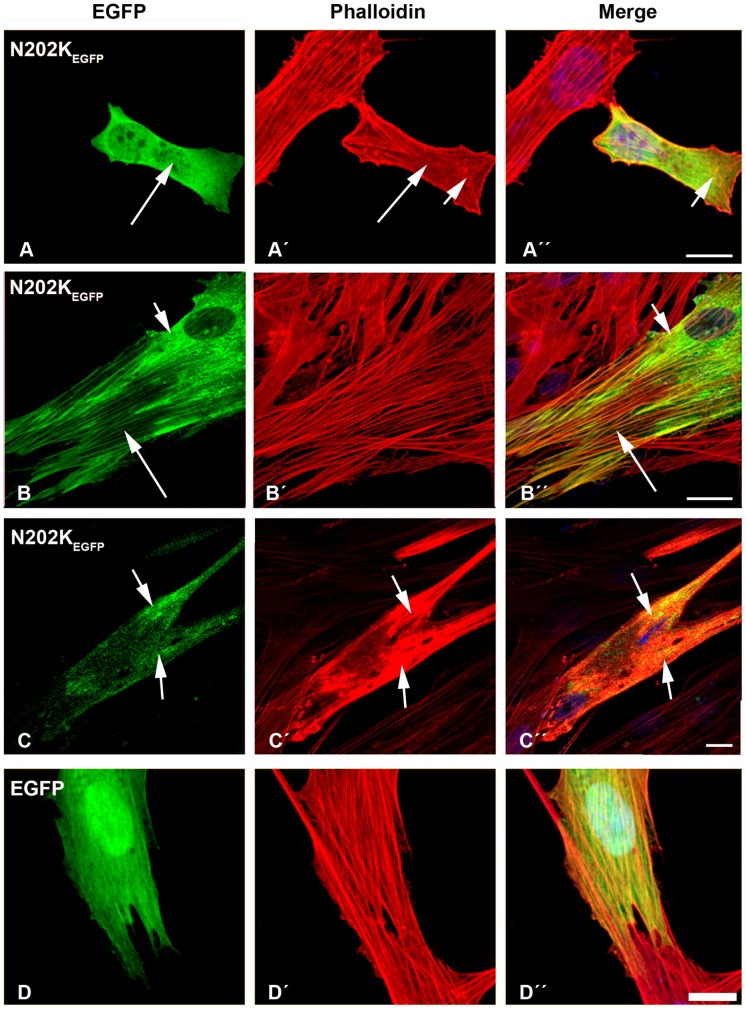
Figure 6. The expression of E202K-β-TMEGFP and empty EGFP constructs in human cells.
The E202K-β-TMEGFP mutant was transfected in human (A–B) myoblasts and (C) myotubes. (D) Empty EGFP construct was transfected in myoblasts. Cells were labeled with TRITC-phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue) to highlight cell nuclei. The transfection of human myoblasts with mutant N202K-β-TM induced the diffuse cytoplasmic labeling of stress fibres (A–A’; long arrows) and small phalloidin-labeled aggregates in the cytoplasm (A’ and A”; short arrows). Mutant N202K-β-TM formed clouds around the nucleus (B and B”; short arrows), in addition to a well-defined organised filamentous structure of stress fibres (B–B”; long arrows). In many N202K-β-TMEGFP-transfected myotubes, more marked changes in actin structures were observed (C–C”). A large accumulation of mutant N202K-β-TM with the co-localisation of polymerised actin appeared, suggesting the disruption of endogenous actin filaments (C–C”; short arrows). Human myoblasts transfected with empty EGFP vector formed well-organised filamentous structures (D–D”). Confocal microscopy was performed using a Zeiss LSM 510 Meta confocal microscope or an LSM 700 inverted Axio Observer.Z1 microscope. Scale bar = 10 µm.