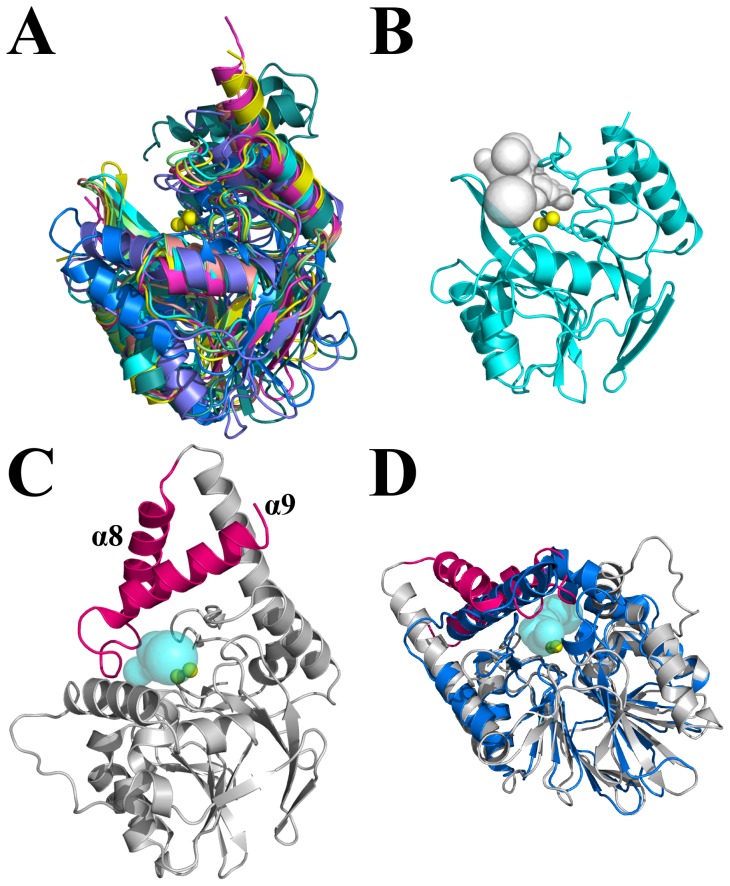
Figure 2. Structural overlays of PqsE homologues adopting the metallo-β-lactamase fold.
A) Conserved active-site localization for eight proteins adopting the metallo-β-lactamase fold (PDB entries 1MQO, 1ZNB, 1JJT, 1KO3, 1X8H, 2YZ3, 1ZTC, and 1QH5). The two conserved active-site metal atoms are depicted as yellow spheres. B) Solvent accessible active-site cavity for a typical member of the metallo-β-lactamase fold (PDB entry 1MQO). The solvent accessible cavity was computed with CAVER [35] and is depicted as a gray surface. C) The α8 and α9 helices (in pink) restrict ligand access to the active site of PqsE by forming a narrow and elongated tunnel. The solvent accessible surface tunnel was computed with CAVER and is shown in cyan (PDB entry 2Q0I). D) Superposition of PqsE (gray) and the structural homologue ST1585 from Sulfolobus tokodaii (blue). ST1585 is the only structurally resolved homologue with such high similarity in the protein core (Cα RMSD of 2.8 Å) and a similar α-helical motif restricting active-site access by forming a narrow tunnel-shaped entrance (cyan surface).