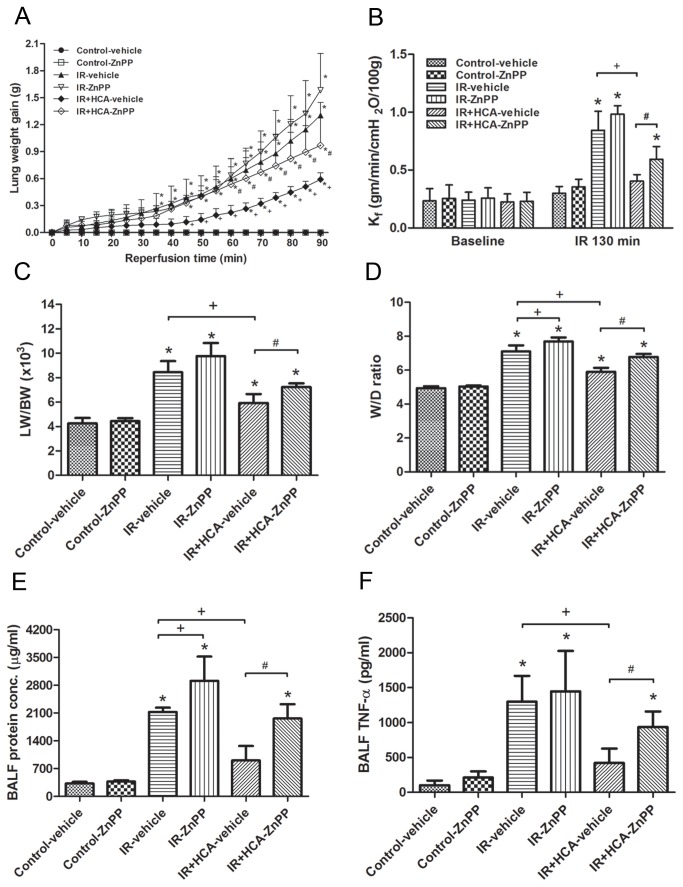
Figure 3. Effect of HCA and ZnPP on pulmonary edema and TNF-α level in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.
The lung weight gain (A), Kf (B), lung weight/body weight (LW/BW) (C) and wet/dry (W/D) weight ratios (D), protein concentration (E) and TNF-α level in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (F) increased significantly in the ischemia-reperfusion (IR) group. The increase in these parameters was significantly attenuated by treatment with HCA. The protective effect of HCA was partially abrogated by ZnPP treatment. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *significantly different from control (P < 0.05); + significantly different from IR-vehicle (P < 0.05); # significantly different from IR+HCA (P < 0.05), using one-way or two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test.