Figure 6. Effect of HCA and ZnPP for IKK-NFκB signaling pathway in lung tissue.
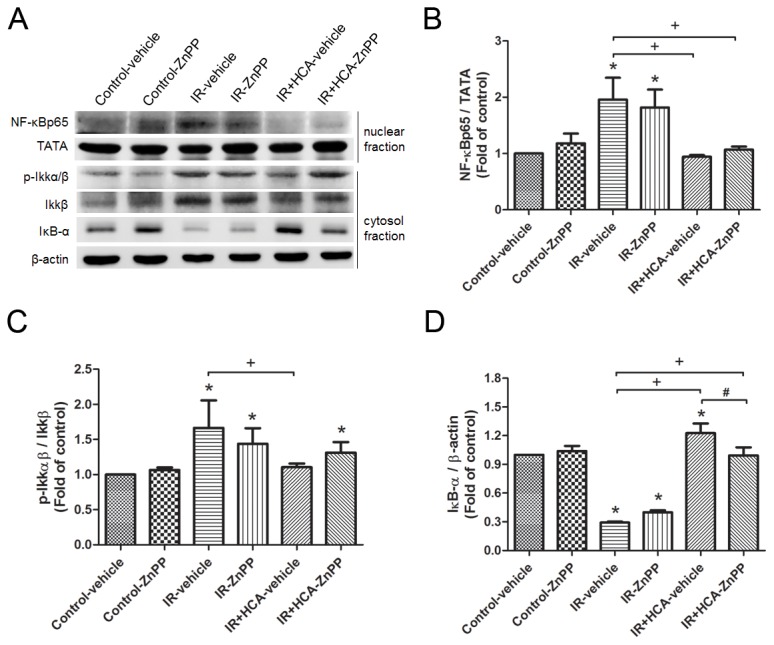
Hypercapnic acidosis (HCA) increased the IκB-α level and reduced cytoplasmic phosphorylated IKK and nuclear NF-κB p65 levels in ischemia-reperfusion (IR)-induced lung injury. Zinc protoporphyrin IX (ZnPP) treatment partially attenuated the protective effect of HCA. TATA and β-actin served as loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, respectively. A representative blot is shown. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *significantly different from control (P < 0.05); +significantly different from IR-vehicle (P < 0.05); # significantly different from IR+HCA (P < 0.05), using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test.
