Figure 2.
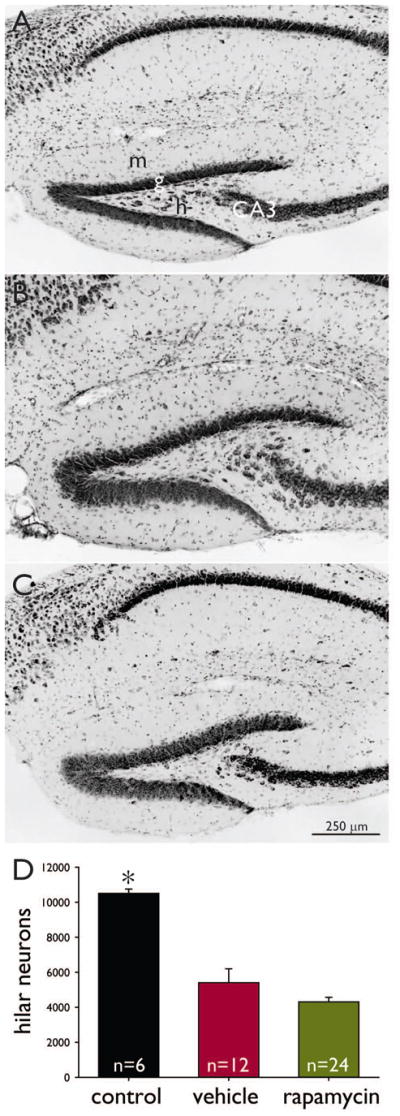
High-dose rapamycin does not prevent hilar neuron loss. Nissl-stained sections of the dentate gyrus of a naïve control mouse (A), a mouse that experienced pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus and was treated with vehicle (B), and a mouse that experienced status epilepticus and was treated with 10 mg/kg rapamycin (C). m = molecular layer, g = granule cell layer, h = hilus, CA3 = CA3 pyramidal cell layer. D Average number of hilar neurons per hippocampus. *p < 0.05 compared to other groups (ANOVA on ranks with Dunn’s method). Vehicle and rapamycin groups are not significantly different. Error bars indicate s.e.m.
