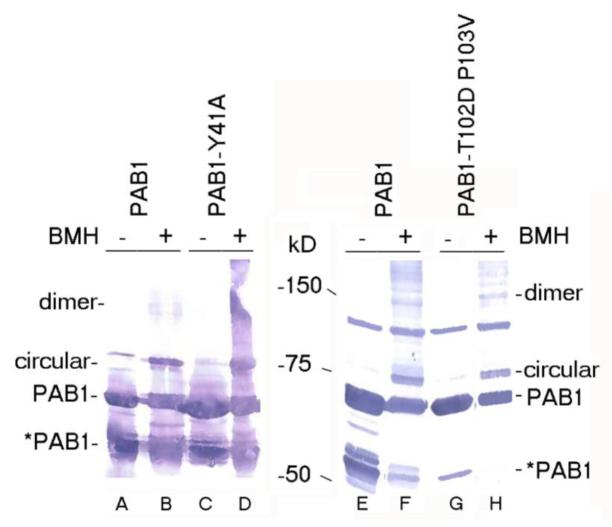
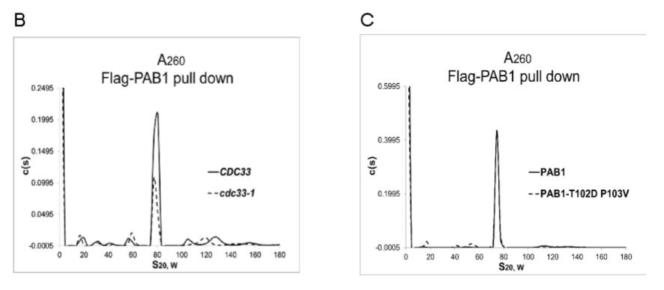
Figure 6.
PAB1-Y41A and –T102D P103V effects on protein interactions. A. BMH cross-linking (+) was compared to mock-treated samples (−). Lanes A and E- PAB1 (mock-treated); lanes B and F- PAB1 (BMH treated); lane C- PAB1-Y41A (mock-treated); lane D- PAB1-Y41A- (BMH treated); lane G- PAB1-T102D P103V (mock-treated); and lane H- PAB1-T102D P103V- (BMH treated). PAB1 proteins were identified by Western analysis using anti-Flag antibody. The circular and linear species of PAB1 are indicated. In lanes A and C, the slower migrating species in the mock-treated samples that nearly co-migrates with the circular form is a non-specific protein detected with the anti-Flag antibody (Yao et al 2007). *PAB1 refers to the C-terminally truncated form of PAB1 (Yao et al 2007). B. AU analysis of Flag-agarose purified yeast extracts containing wild-type PAB1 (CDC33 is strain AS319/YC504 (PAB1) and cdc33-1 is strain AS1881/YC504 that is isogenic to AS319/YC504 except for carrying the cdc33-1 allele). C. Same as ‘B’ above, except PAB1 versus PAB1-T102D P103V are depicted.