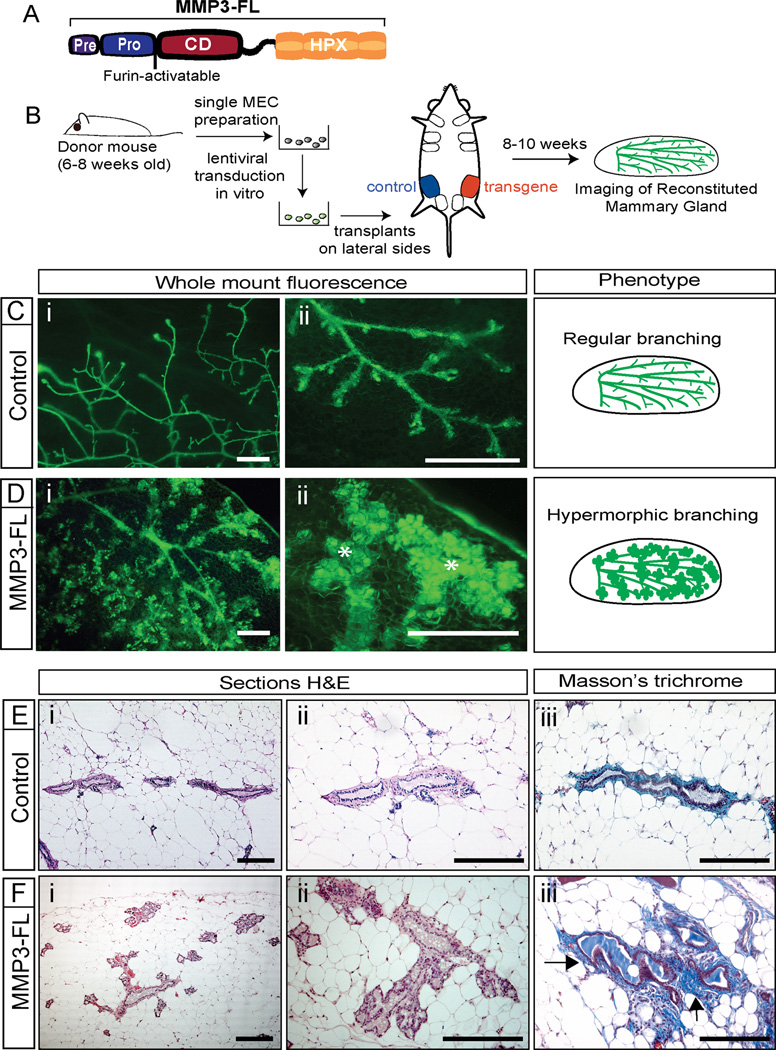
Figure 1. MMP3 Induces Hypermorphic Mammary Epithelial Growth.
(A) Schematic representation of full length MMP3 (MMP3-FL). Pre-domain: signal sequence; Pro-domain; inhibitory peptide that was made cleavable by furin; CD: catalytic domain; HPX: hemopexin-like domain.
(B) Experimental scheme: Single MECs were isolated from donor mice and transduced with either control or transgene expressing viruses. Transduced MECs were transplanted into epithelium-cleared contralateral inguinal mammary fat pads of recipient mice. Reconstituted mammary glands were analyzed 8–10 weeks later by fluorescence microscopy.
(C–D) Representative images showing green fluorescence of whole mount transplants from control (Ci–ii) and MMP3-FL (Di–ii) transduced MECs. MMP3-FL overexpression (n=10) leads to hypermorphic mammary epithelial branching with significantly increased epithelial outgrowth (asterisk) in 9 of 10 transplants, while control transplants (n=10) showed regular epithelial growth and branching in all cases. Schematic depiction of the respective epithelial outgrowth phenotype is shown. Scale bars represent 1 mm.
(E–F) H&E (i–ii) and Masson’s trichrome (iii) stained sections of mammary transplants from control (E) and MMP3-FL (F) transduced MECs. Transplants expressing MMP3-FL displayed strongly increased epithelial branching (i–ii) and prominent deposition of collagen around ductal structures (arrows), as revealed by blue staining in Masson’s trichrome (iii). Scale bars represent 20 µm.
Also see Figure S1.