FIGURE 4.
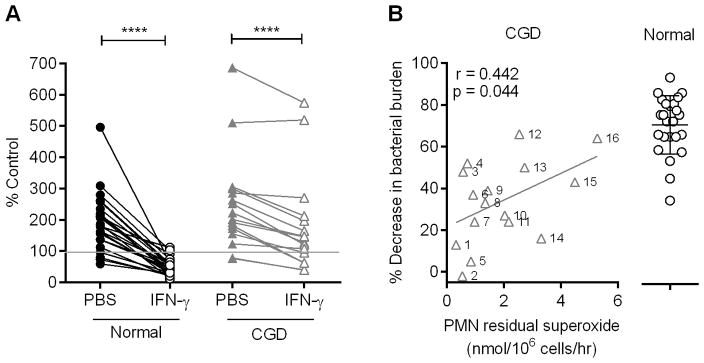
IFN-γ maintains microbicidal activity of normal monocytes and stimulates monocytes from some CGD subjects to control G. bethesdensis growth. (A) Monocytes from normal (n=24) and CGD (n=16) donors were treated with PBS control or 65U IFN-γ/ml for 2 days before infection with G. bethesdensis for 24 hours at an MOI of 1 bacterium per host cell in the presence of autologous serum. Data are represented as % control input. Significance testing of PBS control versus IFN-γ treatment was by Wilcoxon paired t-test (**** = p ≤ 0.0001). (B) Percentage decrease in bacterial burden after IFN-γ treatment relative to PBS control for all normal and CGD monocytes in panel (A). Percentages for CGD monocytes are plotted against residual superoxide in PMN from the same CGD patients. The relationship of the two variables was assessed using a Spearman correlation and the best fit (Y = 6.409X + 21.59) is depicted.
