Figure 2.
The mossy fiber pathway.
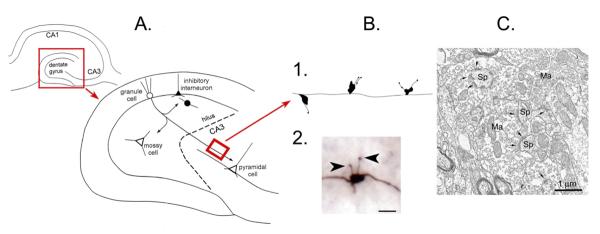
A.
Top left: A schematic or the rodent hippocampus illustrates the location of the major subfields. The area in the red box is expanded to the lower right.
Lower right: The dentate gyrus and area CA3 is shown to illustrate the pathway of the axons of the dentate gyrus granule cells to area CA3 pyramidal cells, the mossy fiber pathway. The mossy fibers collateralize in the hilus where they innervate hilar neurons (mossy cells or inhibitory interneurons) or the hilar dendrites of inhibitory interneurons with cell bodies in the granule cell layer. The main mossy fiber axon innervates pyramidal cells in area CA3 with periodic en passant synapses along the axon, which travels parallel to the CA3 cell layer. Glutamatergic neurons have white cell bodies; inhibitory interneurons are black. The area in the red box is a section from the main mossy fiber axon, expanded in B. From (Scharfman, 2002).
B. 1. A drawing of the periodic massive boutons in stratum lucidum, showing the diversity of irregular shapes of the giant boutons and the diversity in filamentous extensions. 2. A photomicrograph of a mossy fiber bouton from a biocytin-filled granule cell shows the filamentous extensions (arrowheads) that extend from the main bouton. Calibration= 1 μm.
C. An example of a mossy fiber bouton (Ma= massive bouton) contacting spines (Sp) illustrates the complex morphology of the bouton. Kindly provided by Dr. Csaba Leranth.
