Figure 5.
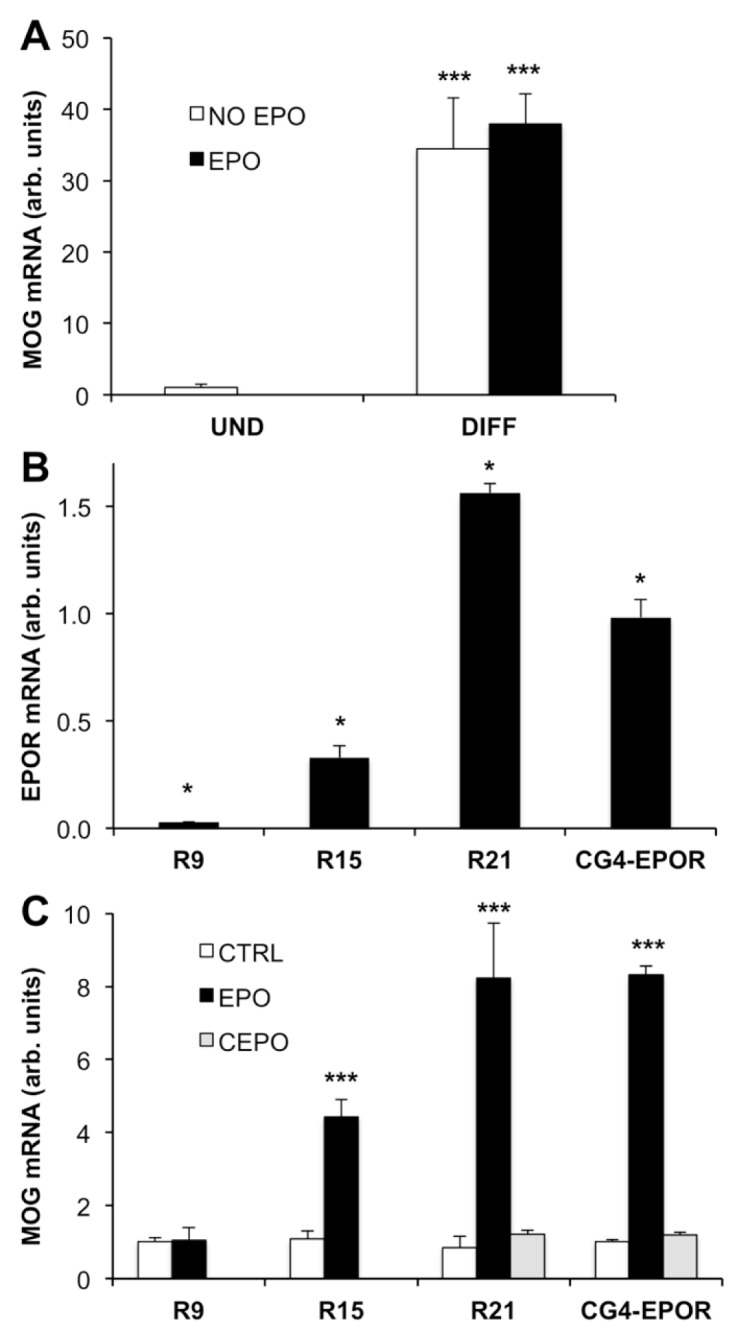
EPO effect is dependent on EPOR expression. (A) EPO has no effect in CG4 cells transduced with the EGFP vector. CG4 cells transduced with EGFP (CG4-EGFP) were differentiated and treated with or without EPO 80 ng/mL. MOG gene expression was analyzed by qPCR at d 5 of differentiation. Results are expressed as arbitrary units versus undifferentiated (UND) cells and are the mean ± SD of four samples analyzed in duplicate. **P < 0.05 versus UND cells by Student t test. (B-C) EPO increases MOG expression in a receptor-dependent manner. (B) Expression of EPOR in three CG4-EPOR clones (R9, R15 and R21) isolated by plating the cells at clonal densities. EPOR expression was measured by qPCR in quadruplicate samples analyzed in duplicate and expressed as arbitrary units versus EPOR expression in the CG4-EPOR cell line. *P < 0.05 by Tukey-Kramer’s test. (C) CG4-EPOR cells and R9, R15 and R21 cell clones were differentiated in the absence or in the presence of EPO 80 ng/mL; CG4-EPOR and R21 were also differentiated in the presence of carbamylated EPO (CEPO) at 80 ng/mL. MOG gene expression was analyzed by qPCR at d 5 of differentiation. Results are expressed as arbitrary units versus no EPO and are the mean ± SD of four samples analyzed in duplicate. ***P < 0.001 versus no EPO by Student t test.
