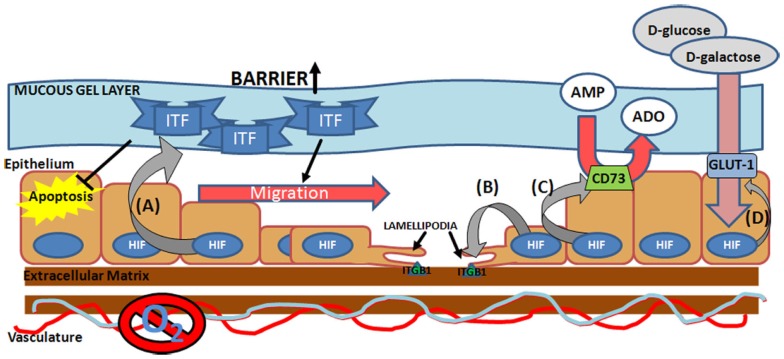
Figure 2.
Hypoxia-inducible factor-mediated pro-restitution pathways. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) activation at the site of the mucosal wound leads to induction of (A) epithelial intestinal trefoil factor (ITF) (33), which acts to increase mucosal barrier function, suppress epithelial apoptosis (127), and drive epithelial migration (80), (B) integrin β1 (ITGB1) (84), a lamellipodia protein critical for epithelial cell migration across the extra-cellular matrix, (C) ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) (38), which facilitates conversion of AMP into adenosine (ADO), and (D) glucose transporter 1 (GLUT-1) (7, 8), which facilitates the transport of D-glucose and D-galactose across the plasma membrane.