Figure 5.
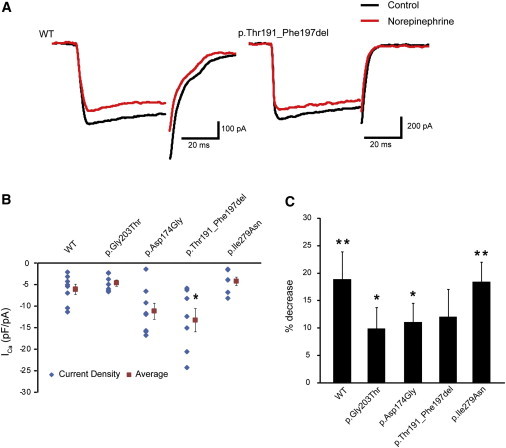
Evaluation of Gαo-Mediated Signaling in NG108-15 Cell Calcium-Current Generation
(A) Representative traces of voltage-gated calcium currents generated in NG108-15 cells expressing WT (left) or p.Thr191_Phe197del altered (right) Gαo1. Black and red traces represent the currents before and 3 min after application of 10 μM norepinephrine, respectively.
(B) Current densities of the calcium currents before norepinephrine treatment in cells expressing WT or altered Gαo1. Scatter plots represent the densities in individual cells. Red squares and bars represent the means and SEMs, respectively, of the densities in individual cell groups (WT, n = 8; p.Gly203Thr, n = 7; p.Asp174Gly, n = 8; p.Thr191_Phe197del, n = 7; p.Ile279Asn, n = 7). Compared with that in cells expressing WT Gαo1, the current density in cells expressing p.Thr191_Phe197del increased significantly (∗p < 0.05 by Dunnett’s post hoc test). The densities in the cells expressing other altered proteins did not vary significantly.
(C) Comparison of norepinephrine-induced inhibition of calcium currents in cells expressing altered Gαo1. Each error bar represents the mean and SEM of the percent decrease in current density induced by application of 10 μM norepinephrine. Paired t tests indicated that the inhibition induced by norepinephrine was significant in cells expressing WT (n = 8) and p.Gly203Thr (n = 7), p.Asp174Gly (n = 8), and p.Ile279Asn (n = 7) altered proteins (∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗p < 0.05), but not in cells expressing p.Thr191_Phe197del (n = 7). Although there was some tendency for decreased inhibition in cells expressing altered proteins, the tendency did not reach statistical significance compared with that in WT-expressing cells (p = 0.41 by ANOVA).
