Figure 5.
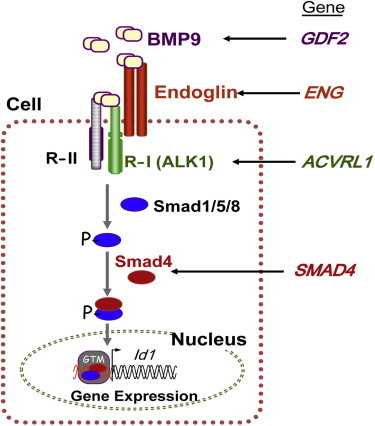
BMP9 and the TGF-β Signaling Pathway
BMP9 binds to specific type I and type II cell-surface receptors (R-I and R-II, respectively) that exhibit serine-threonine kinase activity, as well as to the auxiliary receptor endoglin. Upon ligand binding, R-II transphosphorylates ALK1 (R-I), which then propagates the signal by phosphorylating receptor-regulated (R-Smads) Smad1, Smad5, and Smad8 (“Smad1/5/8”). Once phosphorylated, R-Smads form heteromeric complexes with a cooperating homolog, Smad4, and translocate into the nucleus where they regulate the transcriptional activity of target genes, including Id1. Endoglin, ALK1, and Smad4 are encoded by ENG, ACVRL1 and SMAD4, respectively, whose pathogenic mutations give rise to HHT1, HHT2, and JP-HHT, respectively. BMP9 is encoded by GFDF2, whose pathogenic variants are described here. The following abbreviation is used: GTM, general transcription machinery. This figure was adapted from Figure 2 in Fernández et al.30
